See the answer Find all values of x such that f (x) > 0 and all x such that f (x) < 0 and sketch the graph of f 1) Answer f (x) > 0 if x < 2 or 0< x< 4 ;Use a calculator to graph f(x) Use the graph to solve f(x) > 0 (Enter your answer using interval notation) f(x) = x 5 /(x − 2)(x − 4) f(x) > 0 when x is in Expert Answer Who are the experts?B) Does f have a maximum or minimum value?

Limits
Lim x approaches infinity f(x)=0 graph
Lim x approaches infinity f(x)=0 graph-From the graph of f(x), draw a graph of f ' (x) We can see that f starts out with a positive slope (derivative), then has a slope (derivative) of zero, then has a negative slope (derivative) This means the derivative will start out positive, approach 0, and then become negative Be Careful Label your graphs f or f ' appropriately When we're graphing both functions and theirIf f′(x) < 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is decreasing on (a,b) Suppose c is a critical number of a continuous function f, then Defn f is concave down if the graph of f




The Graph Of F X Is Given In The Figure Below Draw The Lines To The Graph At X 4 X 3 X 0 And X 3 Estimate F 4 F 3 F 0 And F 3 Study Com
the function f of X is graphed find F of negative one so this graph right over here is essentially a definition of our function it tells us given the allowed inputs into our function what would the function output so here they're saying look what does what gets output when we input X is equal to negative one so x equals negative one is right over here X is equal to negative one andWorked example matching a function, its first derivative and its second derivative to the appropriate graphEven a function with a smooth graph is not differentiable at a point where its tangent is vertical For instance, the function given by f(x) = x 1/3 is not differentiable at x = 0 In summary, a function that has a derivative is continuous, but there are continuous functions that do not have a derivative
X is not equal to 0 or 1 Please explain how to get all values of x when f (x) > 0 and f (x For example, if f is a function that has the real numbers as domain and codomain, then a function mapping the value x to the value g(x) = 1 / f(x) is a function g from the reals to the reals, whose domain is the set of the reals x, such that f(x) ≠ 0 The range of a function is the set of the images of all elements in the domainSince f(−x) = e− (− x) 2 2 = e− 2 = f(x) and lim x→±∞ e− (−x)2 2 = 0, the graph is symmetry wrt the yaxis, and the xaxis is a horizontal asymptote • Wehave f0(x) = e−x 2 2 (−x) = −xe− x2 2 • Thus f ↑ on (−∞,0) and ↓ on (0,∞) • Atx = 0, f 0(x) = 0 Thus f(0) = e = 1 is the (only) local and
Free graphing calculator instantly graphs your math problemsThe graph of f'(x) the derivative of j{x) is shown in each of the following questions Answer the Positive Does not exist Negati,e 0 I Kegative F"(x) Positi,·e Does not Exist Positi,·e 0 I l\egative 1t Al what value(s) of x does Fha,·e relative extrema?Let g (x) = x 0 f (t) dt, where f is the function whose graph is shown Two line segments and a curve are connected to form the function labeled f on the t y coordinate plane The first line segment starts on the yaxis at the value y = 1, goes down and right crossing the taxis at t = 1, and ends at the point (2, −1)



College Algebra Is The Product Of Real Linear Factors But If F X 0 Has Imaginary Or Complex Roots F X Containsquadratic Factors Of The Type X A 6 Which Cannot
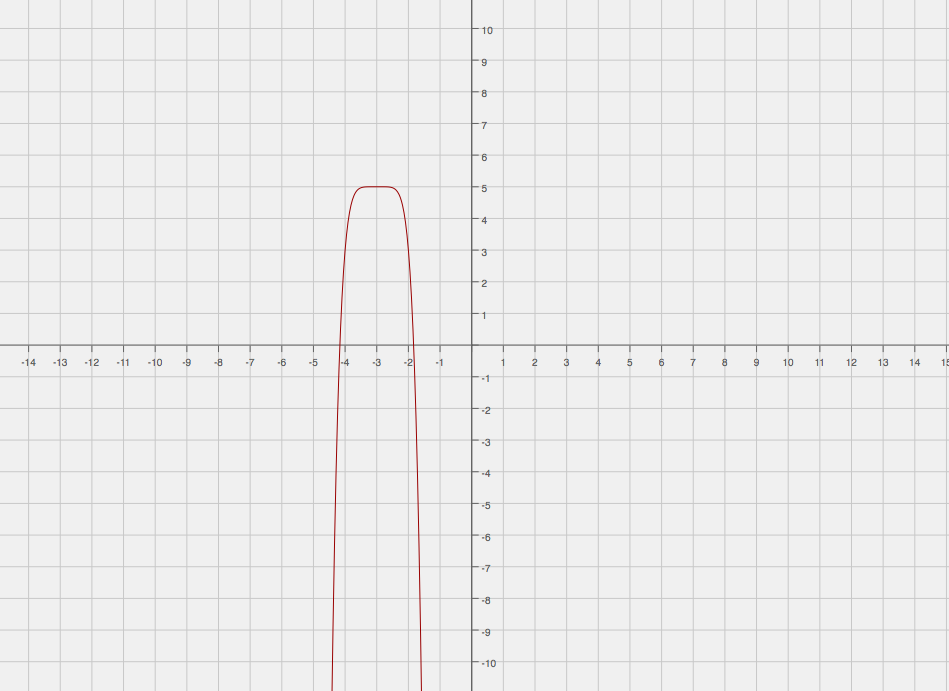



How Do You Sketch The Graph That Satisfies F X 0 When X 3 F X 0 When X 3 And F 3 5 Socratic
Answer to Sketch the graph of a function that satisfies f'(x) 0 \\\\f''(x) 0 if x 2 and f''(x) 0 if x 2 , f has inflection point (2,5)So we have the graphs of two functions here we have the graph y equals f of X and we have the graph y is equal to G of X and what I want to do in this video is evaluate what G of f of F let me do the F of in another color F of negative five is f of negative five is and it can sometimes see a little daunting when you see these composite functions you're taking you're evaluating the function GC < 0 moves it down




10 Points Sketch A Graph Which Has All Of The Foll Gauthmath
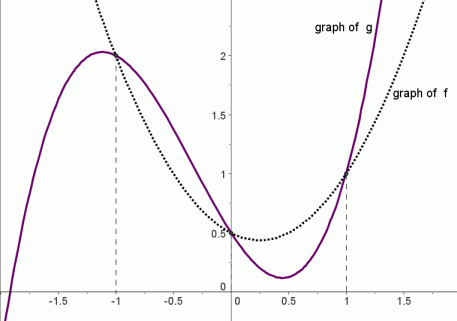



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X G X And F X G X
Graph f (x)=2x f (x) = 2x f ( x) = 2 x Rewrite the function as an equation y = 2x y = 2 x Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept y = m x b y = m x b Find the values of m m and b b using2) Sketch the graph of a function whose first and second derivatives are alwaysOn what interval is f decreasing?




Limits
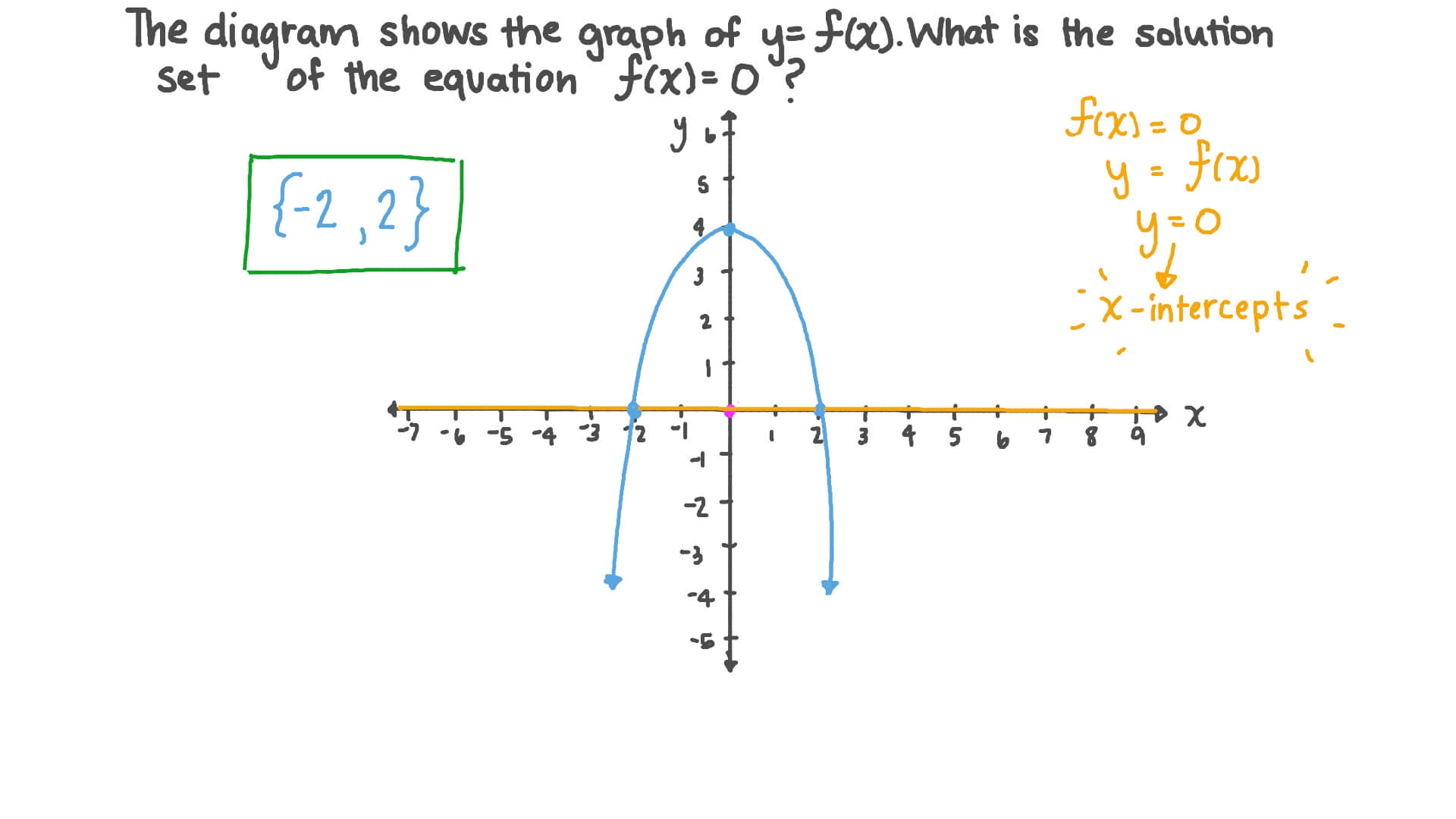



Question Video Finding The Solution Set Of A Quadratic Equation Graphically Nagwa
Linear functions have the form f(x) = ax b, where a and b are constants In Figure 111, we see examples of linear functions when a is positive, negative, and zero Note that if a > 0, the graph of the line rises as x increases In other words, f(x) = ax b is increasing on ( − ∞, ∞)Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Functions of graphs can be transformed to show shifts and reflections Graphic designers and 3D modellers use transformations of graphs to design objects and images (0, 4) \(f(x)\) goes
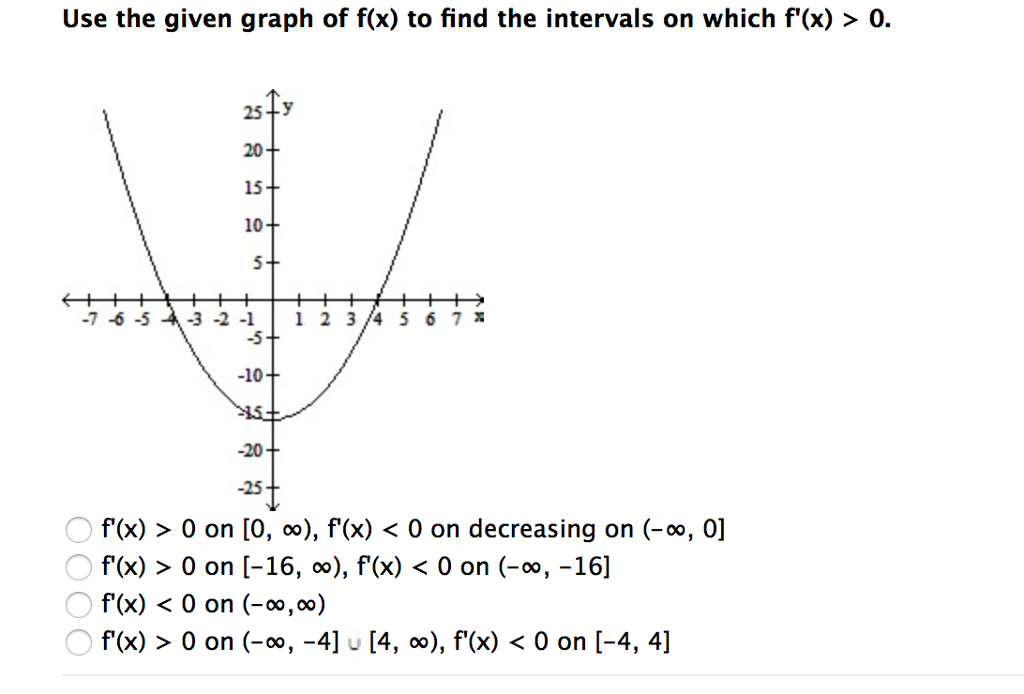



Use The Given Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals On Chegg Com



Solving Polynomial Inequalities By Graphing
E) If f'(x)=0, then the x value is a point of inflection for f To illustrate these principles, consider the following problems 1) Suppose a) On what interval is f increasing?Case 3 p = 1 If p = 1, the power function reduces to the linear function f ( x) = x This case separates the behavior of f ( x) = xp for 0 < p < 1 and p > 1 Case 4 p > 1 The graph of the function is concave up and f ( x) → ∞ as x → ∞ One important feature of power functions is how they compare to one another whenThe graph always lies above the xaxis, but becomes arbitrarily close to it for large negative x;




Derivative And Tangent Line




The Graph Of Fx Is Depicted On The
Use a graph of f(x) to determine the value of f(n), where n is a specific xvalueTable of Contents0000 Finding the value of f(2) from a graph of f(x)002So we substitute 0 in for f(x) and we get Now we solve for x Add 12 to both sides Divide both sides by 3 This will isolate x So if we let x=4 we should get f(x)=0, in other words, f(4)=0 So lets verify this Check Plug in x=4 works This verifies our answer Here you can see the graph of and the xintercept of (4,0)Absolute Value and Distance




Match The Conditions F X Less Than 0 And F X Less Than 0 With One Of The Graphs In The Figure Study Com




At Which Point On The Graph Of Y F X Shown Abov Gauthmath
It represents the y intercept of f(x) Let's understand this with an example Let f(x)=4x5 If you graph it the function looks like this Now f(0) right?Many times you will be given the graph of a function, and will be asked to graph the derivative without having the function written algebraically Here we gi Piecewise functions can be split into as many pieces as necessary Each piece behaves differently based on the input function for that interval Pieces may be single points, lines, or curves The piecewise function below has three pieces The piece on the interval f ( x) = 3 x 5 f (x)=3x5 f (x) = 3x5




The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below What Are All Of The Real Solutions Of F X 0 Brainly Com



Search Q Point Of Inflection Tbm Isch
Classify the extrema by type and give a reasonGraph f (x)=100 (07)^x f (x) = 100(07)x f ( x) = 100 ( 07) x Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote The equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 y = 0 Horizontal Asymptote y = 0 y = 0Calculus questions and answers;




Why Isn T F X X Cos Frac Pi X Differentiable At X 0 And How Do We Foresee It Mathematics Stack Exchange
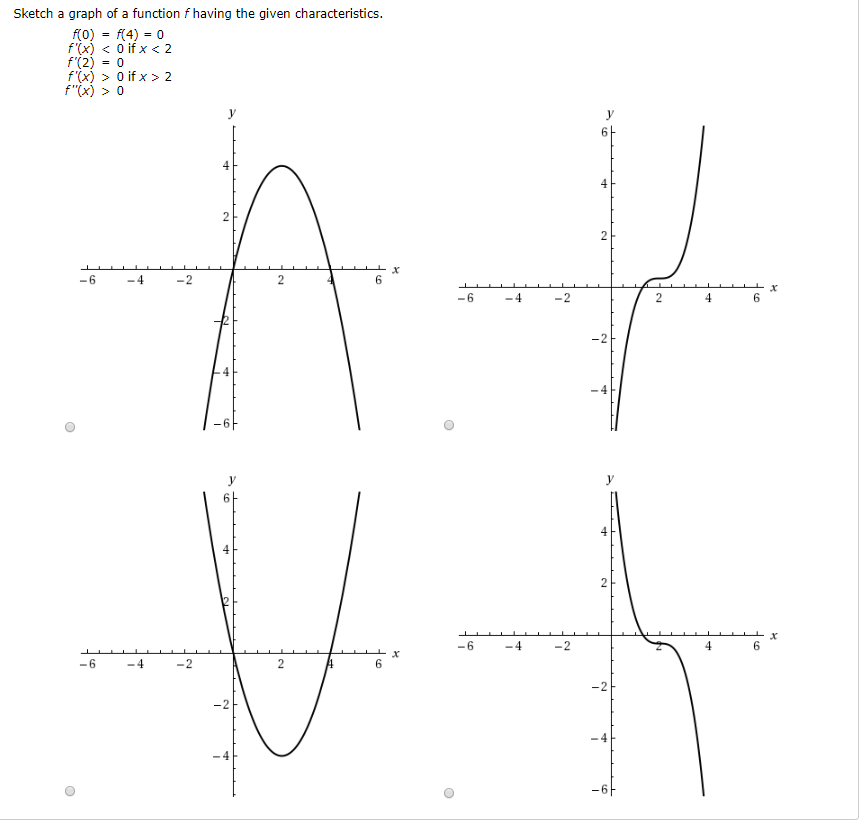



Sketch A Graph Of A Function F Having The Given Chegg Com
So the graph of f(x) isThus, the xaxis is a horizontal asymptote The equation d d x e x = e x {\displaystyle {\tfrac {d}{dx}}e^{x}=e^{x}} means that the slope of the tangent to the graph at each point is equal to its y coordinate at that pointExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high




The Graph Of The Function F X Is Shown Below When F X 0 Determine X Brainly Com



Pathological Taylor Series Stuff
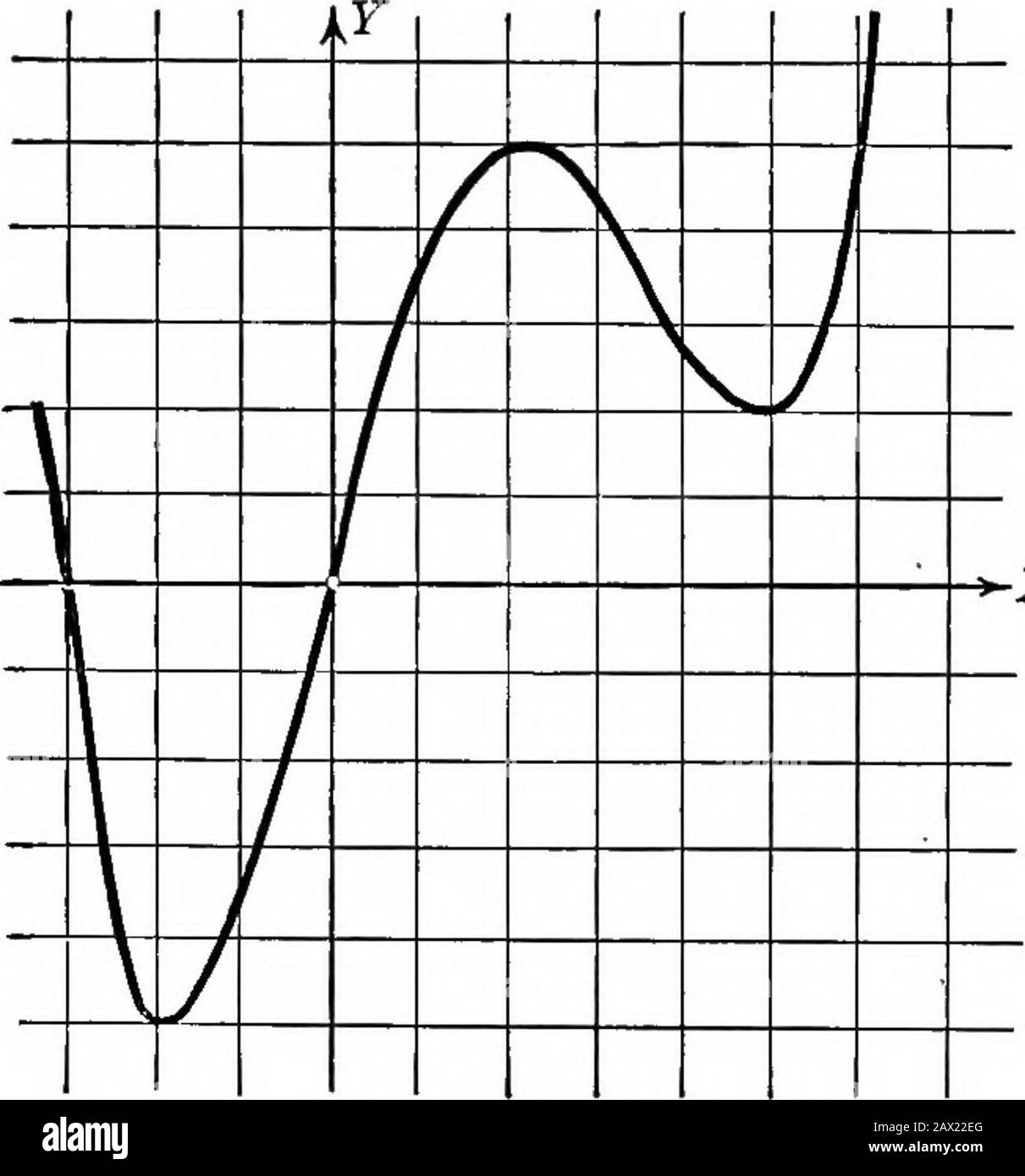
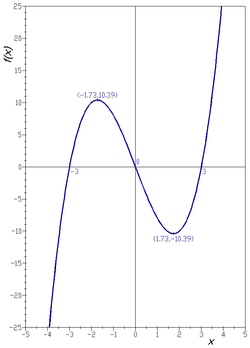
Sketch a graph of the function f that is continuous on (00,00) and has the following properties f'(x) > 0, f''(x) > 0 Choose the correct graph belowF (x) < 0 if 2 < x< 0 or x > 4 2) Answer f (x) > 0 if x > 2 f (x) < 0 if x < 2 ;F X Max 2 X 2 X 4 X Belongs To R Is Family y = Ax A 3 of curves represented by the differential equation of degree Fifteen Persons Among Whom Are A And B Sit Down At Random At A Round Table The Probability That There Are 4 Persons Between A And B Is
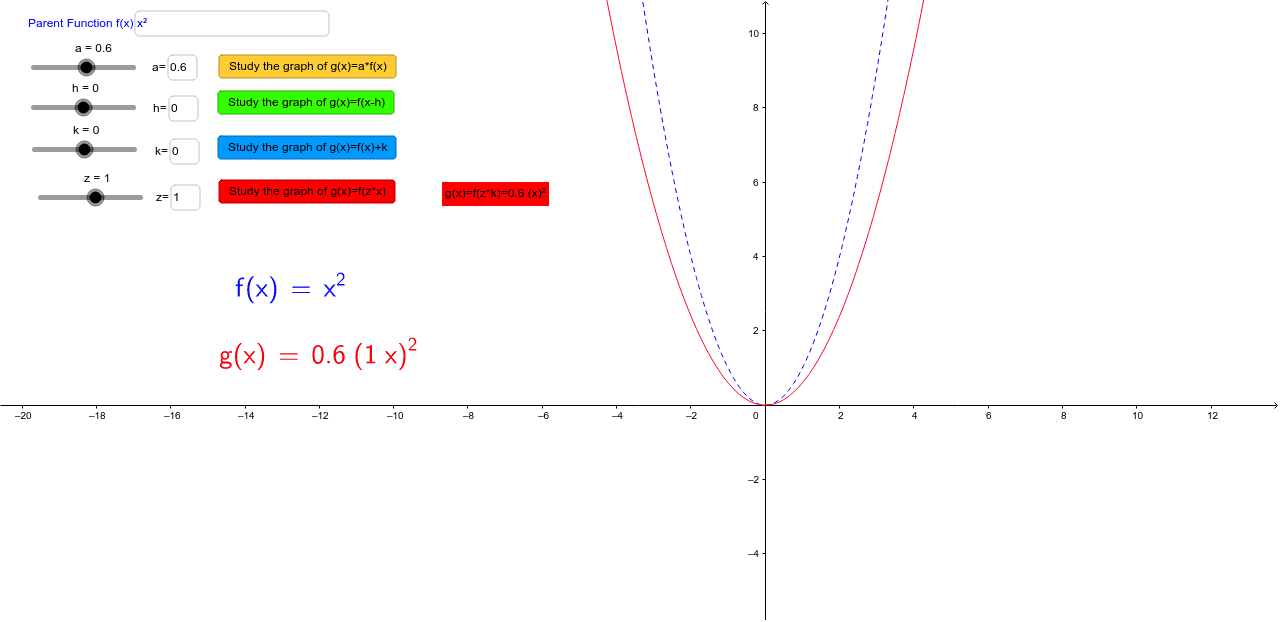



Graph Transformations Discovering Manipulating Functions Geogebra




Derivative And Tangent Line
Sketch the graph of a function f(x) that satisfy the following properties f(x) < 0 for xe( 0, 1)U(5,0) f'(x) > 0 for xe( 1, 3)U(6,0) f(x) = = 00 f(x) = 0 f"(1) = f (5) = 0 2 Find the values of a and b if the function f(x) = r ax bx10 and then increases, and f(1) = 29 to x=6 and f(x) decreases 4A General Note Graphical Interpretation of a Linear Function In the equation latexf\left(x\right)=mxb/latex b is the yintercept of the graph and indicates the point (0, b) at which the graph crosses the yaxis;This video explains how to determine if the function value, first derivative function value, and second derivative function value is positive, negative, or z



Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity




Use The Graph Of F To Determine Where A F X 0 And Chegg Com
2 Answers2 So f ( 6) = ∫ 0 6 f ′ ( x) d x f ( 0) To find the integral we must find the area above the xaxis and the curve and subtract the area below the xaxis and the curve So f ( 6) = 8 7 = 15 Since the derivative is greater than 0 on all x excluding x = 2, we know the function is increasing until it gets to x= 2, where it plateaus, and then it starts increasing again A perfect example of this would be the cubic function f(x) = (x 2)^3 1, as pictured in the following graph Hopefully this helps!Graph of z = f(x,y) New Resources Absolute value of an integer;




2 4 Function Compilations Piecewise Combinations And Composition Mathematics Libretexts
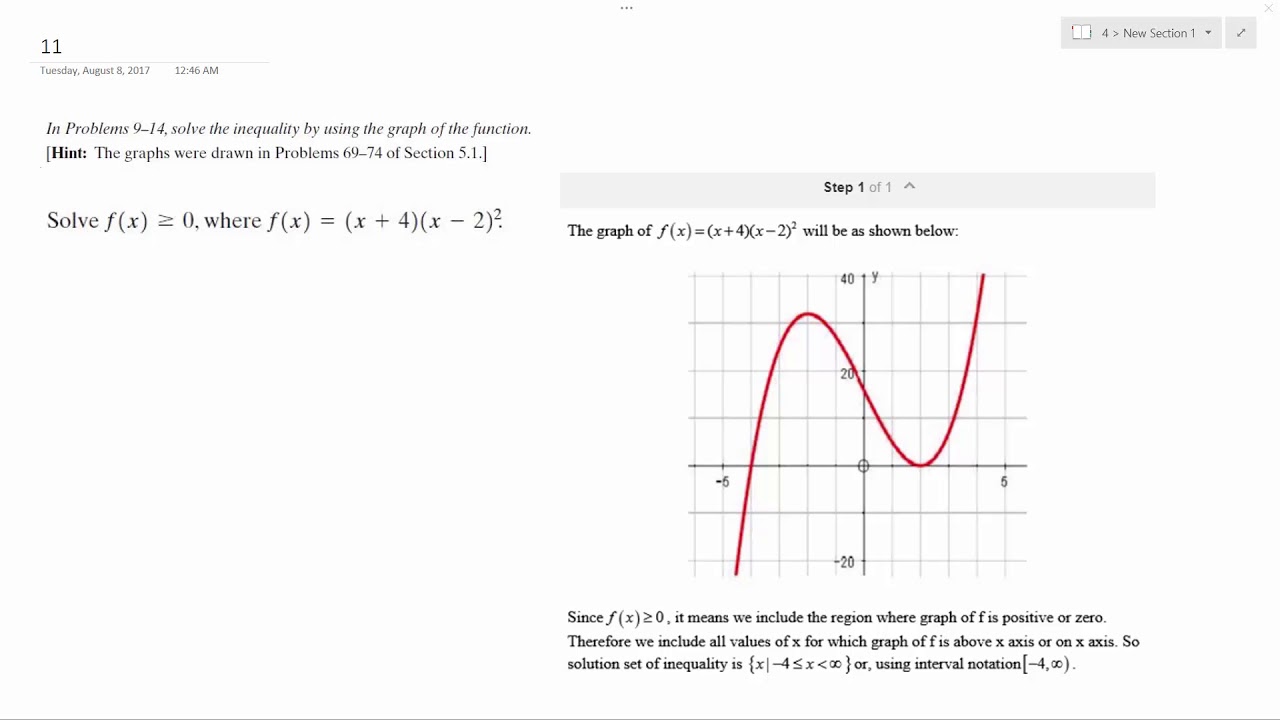



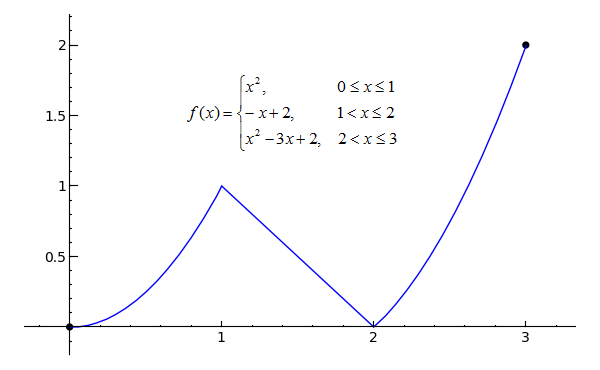
Solve F X Greater Than 0 Where F X X 4 X 2 2 Youtube
Graph f (x)=0 f (x) = 0 f ( x) = 0 Rewrite the function as an equation y = 0 y = 0 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept y = m x b y = m x b Find the values of m m and b b using theAnswer to Sketch a graph of the function f that is continuous Math;The graph of a function $\,f\,$ is shown at right The solution set of the inequality '$\,f(x)\gt 0\,$' is shown in purple It is the set of all values of $\,x\,$ for which $\,f(x)\,$ is positive




Efofex Software



From The Graph Shown Find A F 1 B F 0 C 3f 2 D The Value Of X That Corresponds To F X 0 Math Homework Answers
Before we begin graphing, it is helpful to review the behavior of exponential growth Recall the table of values for a function of the form f (x) = b x f (x) = b x whose base is greater than one We'll use the function f (x) = 2 x f (x) = 2 x Observe how the output values in Table 1 change as the input increases by 1 1For an example of finding and using the second derivative of a function, take f(x) = 3x3 ¡ 6x2 2x ¡ 1 as above Then f0(x) = 9x2 ¡ 12x 2, and f00(x) = 18x ¡ 12 So at x = 0, the second derivative of f(x) is ¡12, so we know that the graph of f(x) is concave down at x = 0 Likewise, at x = 1, the second derivative of f(x) is f00(1) = 18 ¢1¡12 = 18¡12 = 6;Graph f (x)=x Find the absolute value vertex In this case, the vertex for is Tap for more steps To find the coordinate of the vertex, set the inside of the absolute value equal to In this case, Replace the variable with in the expression The absolute value is the distance between a number and zero The distance between and is




The Graph Of A Derivative F X Is Shown In The Figure Below Fill In The Table With Values For F X Given That F 0 8 Begin Array L L L L L L L L Hline X 0 1



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;Solution For The graph of the function y=f(x) passing through the point (0,1) and satisfying the differential equation (dy)/(dx)ycosx=cosx is such that (a) it is a constant function (b) it Notice that the graph of $f$ crosses the $x$axis at $3,2,0,2$ and $3$ Using the fact $f(x)>0$ on the interval where the graph is above the $x$axis, and $f(x)



1



Solving Polynomial Inequalities By Graphing
Closed graph theorem for setvalued functions — For a Hausdorff compact range space , a setvalued function → has a closed graph if and only if it is upper hemicontinuous and F(x) isM is the slope of the line and indicates the vertical displacement (rise) and horizontal displacement (run) between each successive pair of points1) If f '(x) > 0 on an interval I, then the graph of f(x) rises as x increases 2) If f '(x) 0 on an interval I, then the graph of f(x) falls as x increases 3) If f '(c) = 0, then the graph of f(x) has a horizontal tangent at x = c The function may have a local maximum or minimum value, or a point of inflection




Use The Graph Of F X To Find The Solutions To The Equation F X 0 Brainly Com




I Can Sketch The Graph Of F Given The Graph Of F Ppt Download
Functions & Graphing Calculator \square!




Graphs Of F X F X F X And X 0 F T Dt For Example 29 5 Download Scientific Diagram



Search Q Derivative Graph Tbm Isch




Use The Given Graph Of F X To Determine The Intervals Where F X Greater Than 0 F X Less Than 0 The X Values Where F X 0 And Where F X Is
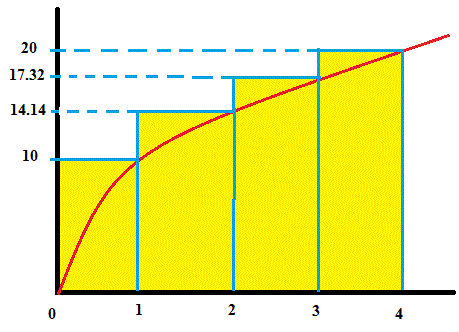



How Do You Estimate The Area Under The Graph Of F X 10sqrt X From X 0 To X 4 Using Four Approximating Rectangles And Right Endpoints Socratic




Draw Graph Of The Function F Defined By F X 1 X X 0 1 Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com
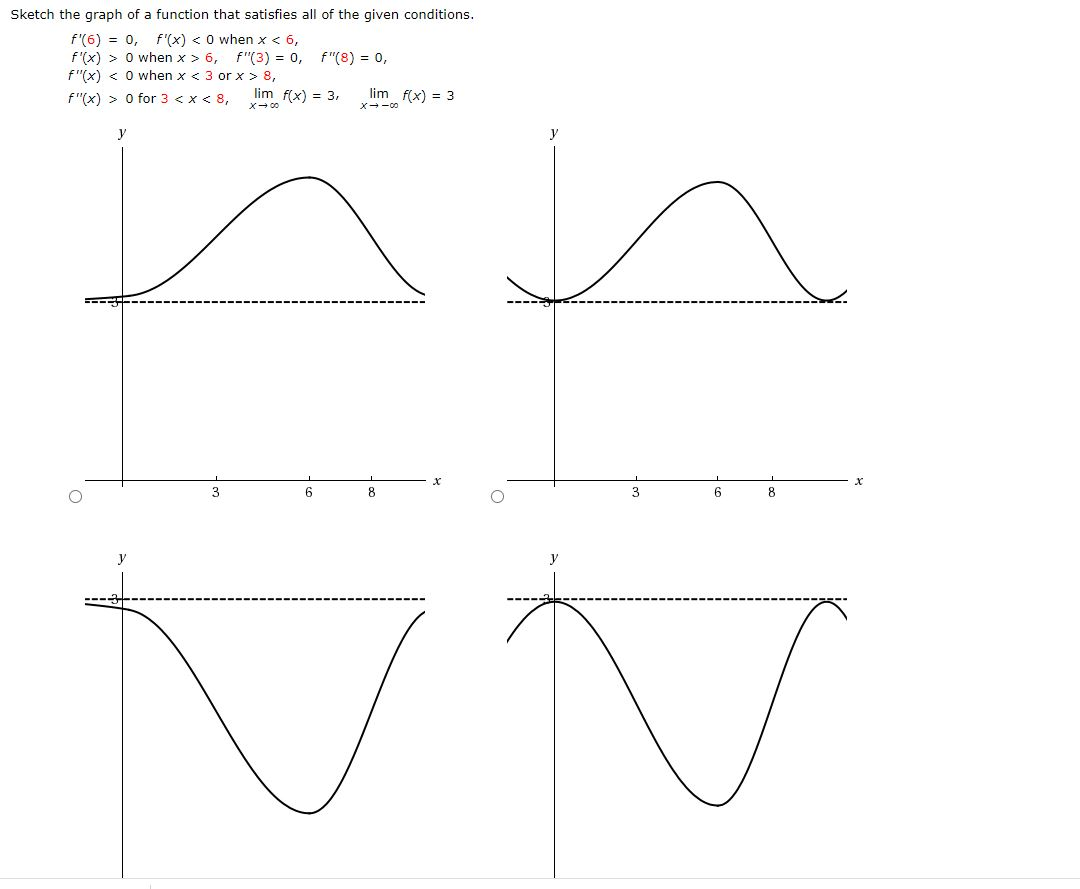



Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com




4 3 Connecting F And F With The Graph Of F Magic Light Calculus




Find The Integral Of F X Dx Evaluated From X 0 To X 3 For The Graph Of Y F X Given Below Study Com
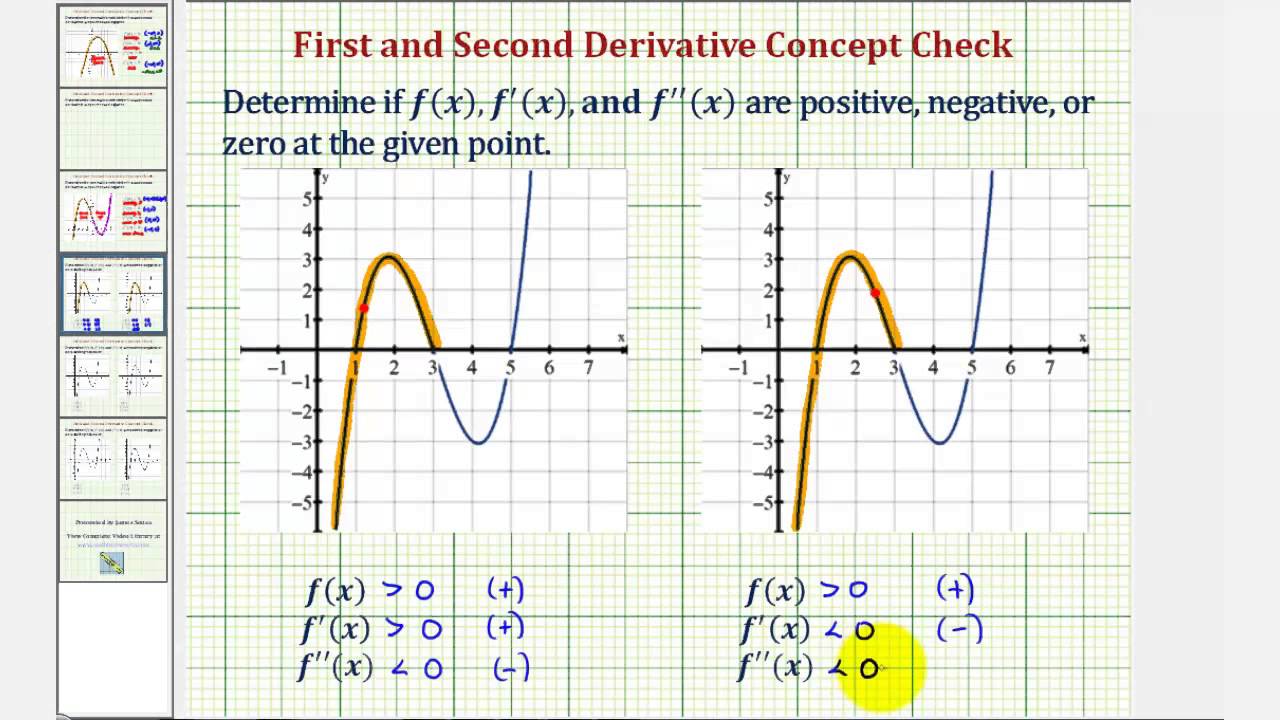



Ex Determine The Sign Of F X F X And F X Given A Point On A Graph Youtube



Let F X 0 If X Is Less Than 5 F X 2 If X Is Greater Than Or Equal To 5 But Less Than 1 F X 4 If X Is Greater Than Or



Calc 1 F X 0 If X 0 What Does This Mean Physics Forums




Graph Of The Function F X From 1 Download Scientific Diagram



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
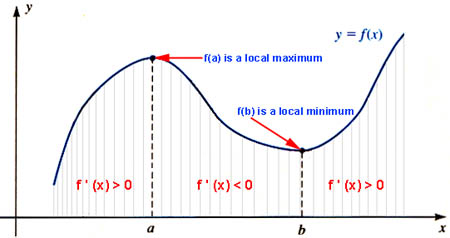



Untitled Document




Each Of The Following Graphs Represent Y F X Find The Indicated Value For Each Of The Following From The Graph Mathematics Stack Exchange




The Graph Of The Function F X Is Shown Below Use The Letters Shown On The Graph To Answer The Following Questions A Find The Value S Of X Where F X 0 B
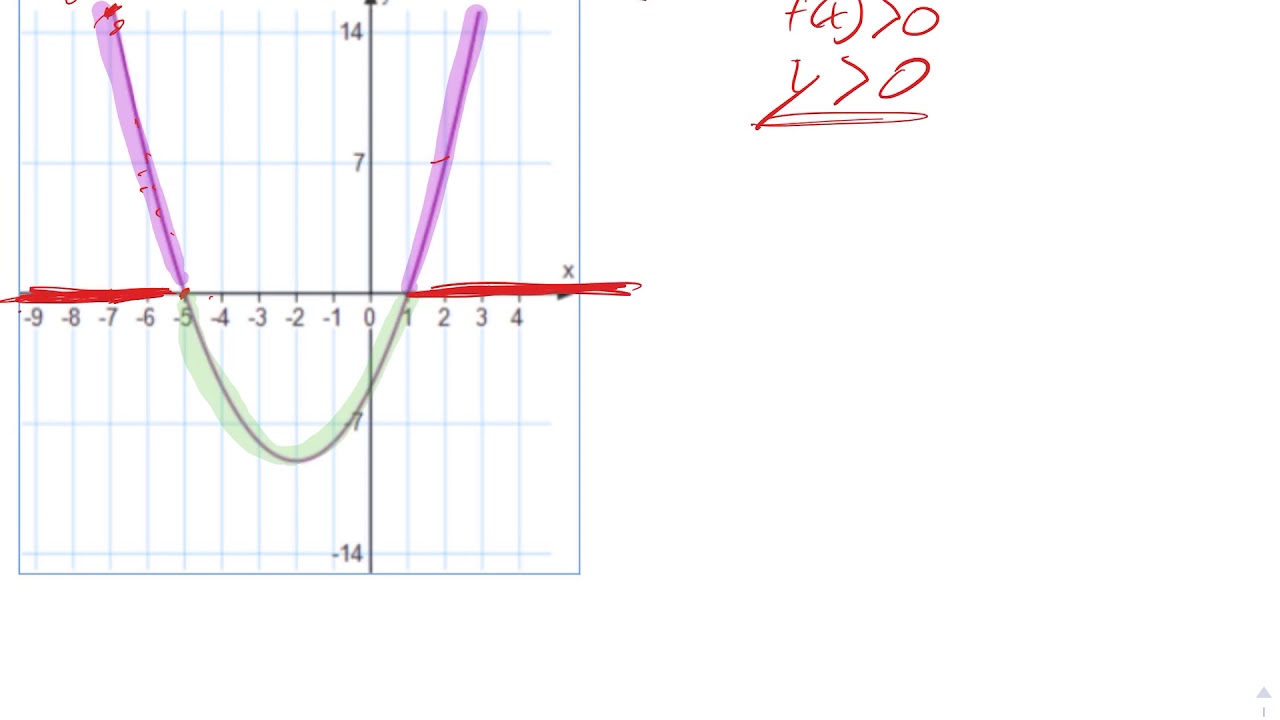



Quadratic Example For What Values Of X Is F X Greater Than 0 Youtube
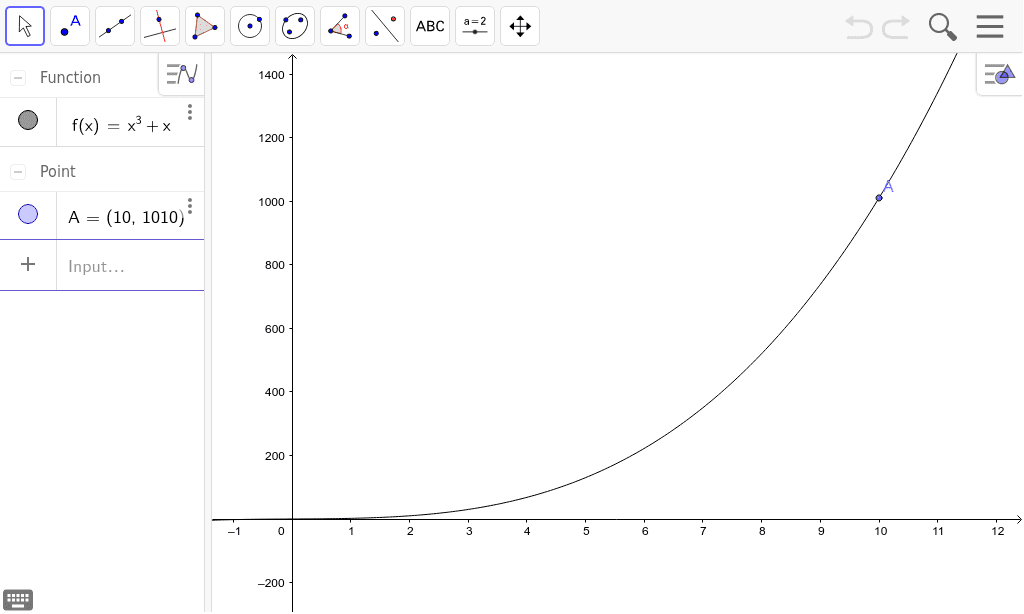



Graph Of F X X 3 X 0 X 10 Geogebra
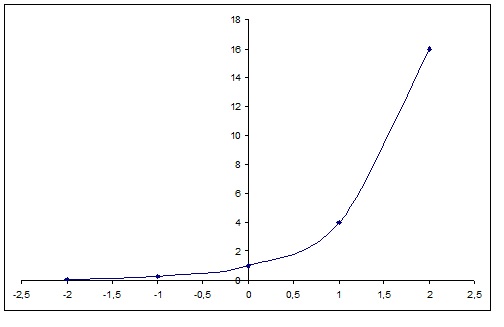



How Do You Graph F X 4 X Socratic




The Graph Of F X Is Given In The Figure Below Draw The Lines To The Graph At X 4 X 3 X 0 And X 3 Estimate F 4 F 3 F 0 And F 3 Study Com




Given By A Graph Is The Function F X How Many Solutions Does F F F X 0 Have Mathematics Stack Exchange




Question Video Finding The Solution Set Of A Quadratic Equation Graphically Nagwa



Solution Graph The Piecewise Function Show All Work F X X If X Amp 04 0 And 0 If 0 Lt X Lt 5 And 2x 10 If X Amp 05 5 State Whether The Function Is Continuous If It Is
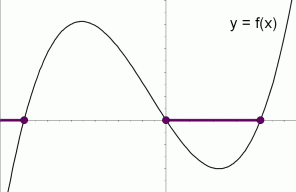



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
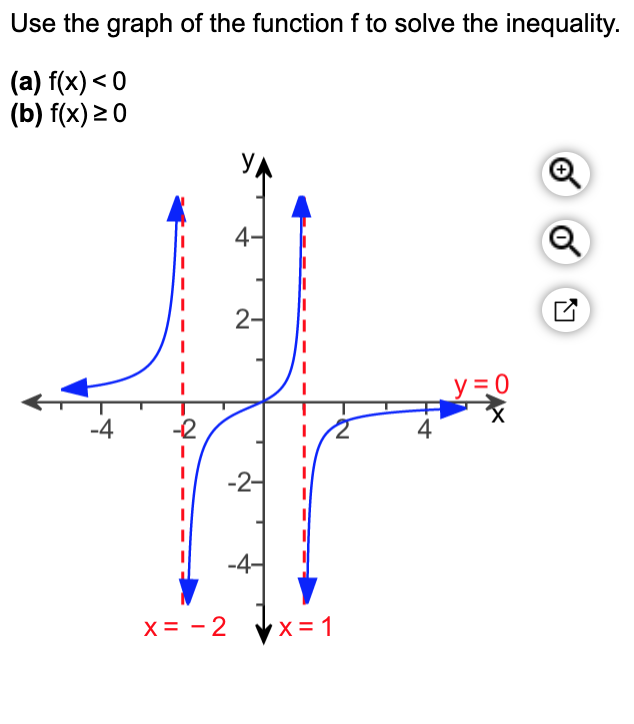



Answered Use The Graph Of The Function F To Bartleby



Graphing A Function Using The First Derivative Graph Math100 Mirka




Sketch The Graph Of F X0 X 2 4 X 2 X 6 Be Study Com




The Graph Of F X Is Given Below Use This Graph To Find The Average Value Of F X From X 0 To X 7 Study Com
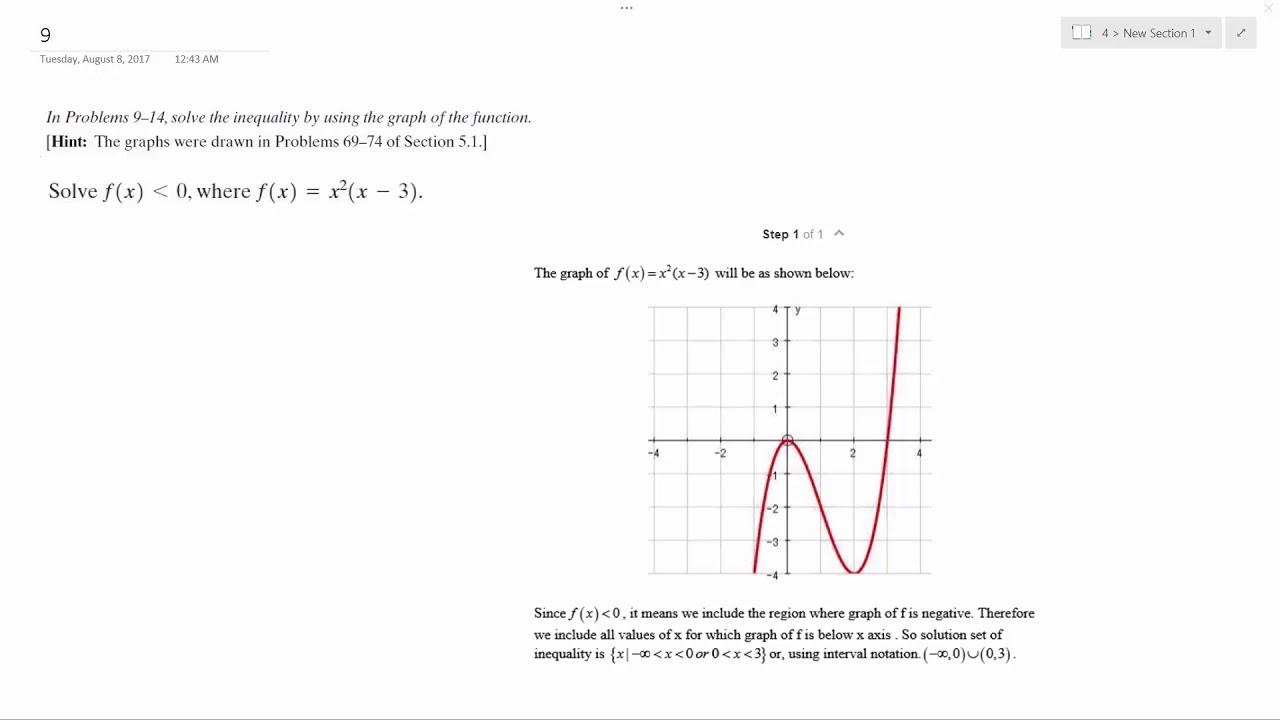



Solve F X Less Than 0 Where F X X 2 X 3 Youtube




Graphing Transformations Of Logarithmic Functions College Algebra




Graph Of The Function Zx Z M X Z F X Vs X For Various Values Of Download Scientific Diagram



Graphs Of Functions




Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies The Following Conditions F 2 F 2 0 F X Less Than 0 For X Less Than 2 F X Greater Than 0 If 2 Less



1
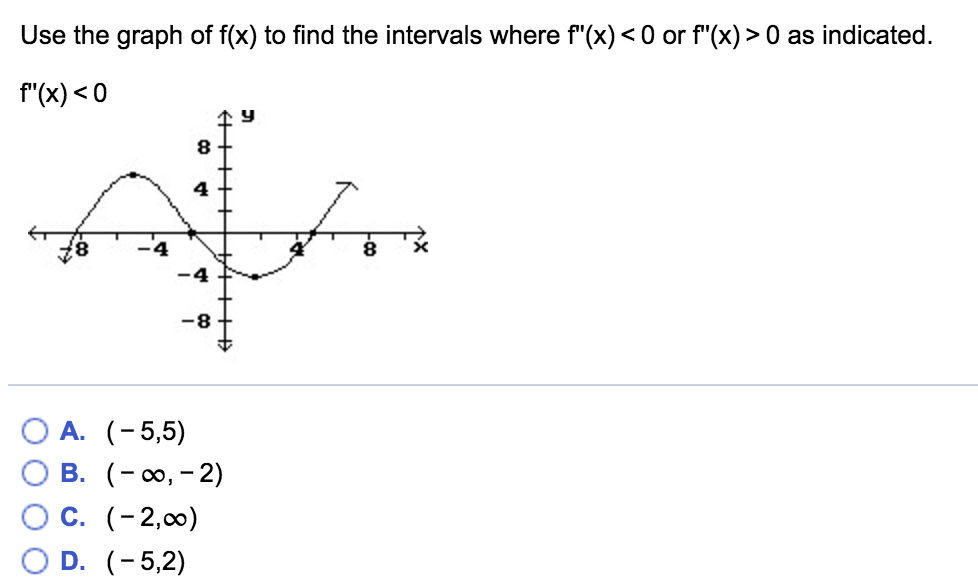



Use The Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals Where Chegg Com
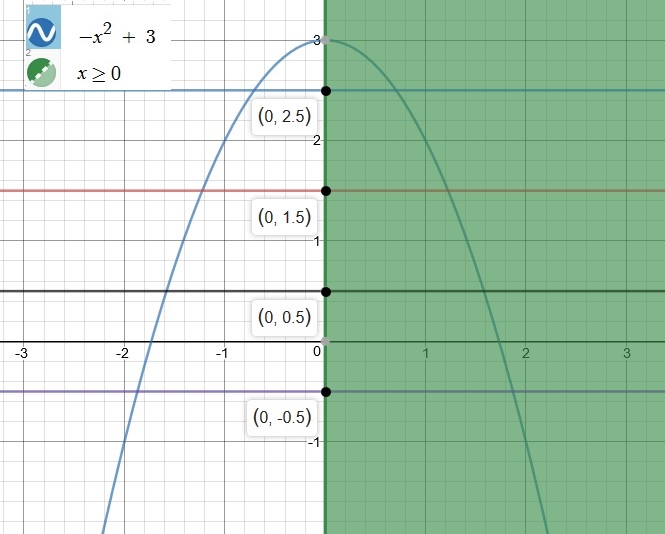



How Do You Graph F X X 2 3 X 0 And Then Use The Horizontal Test To Determine Whether The Inverse Of F Is A Function Socratic



How To Sketch The Graph F X In The Range 3pi 3pi Where F X Cos X Pi X 0 And Cos X 0 X Pi Quora
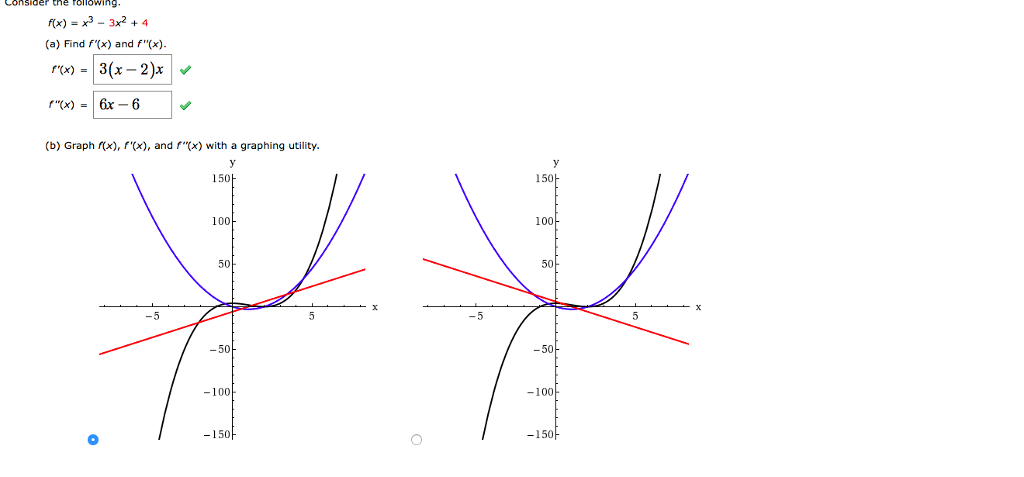



C Identify X Values Where F X 0 Enter Your Chegg Com




The Graph Of F Is Locally Linear At X 0 As Is Suggested By Zooming In Download Scientific Diagram
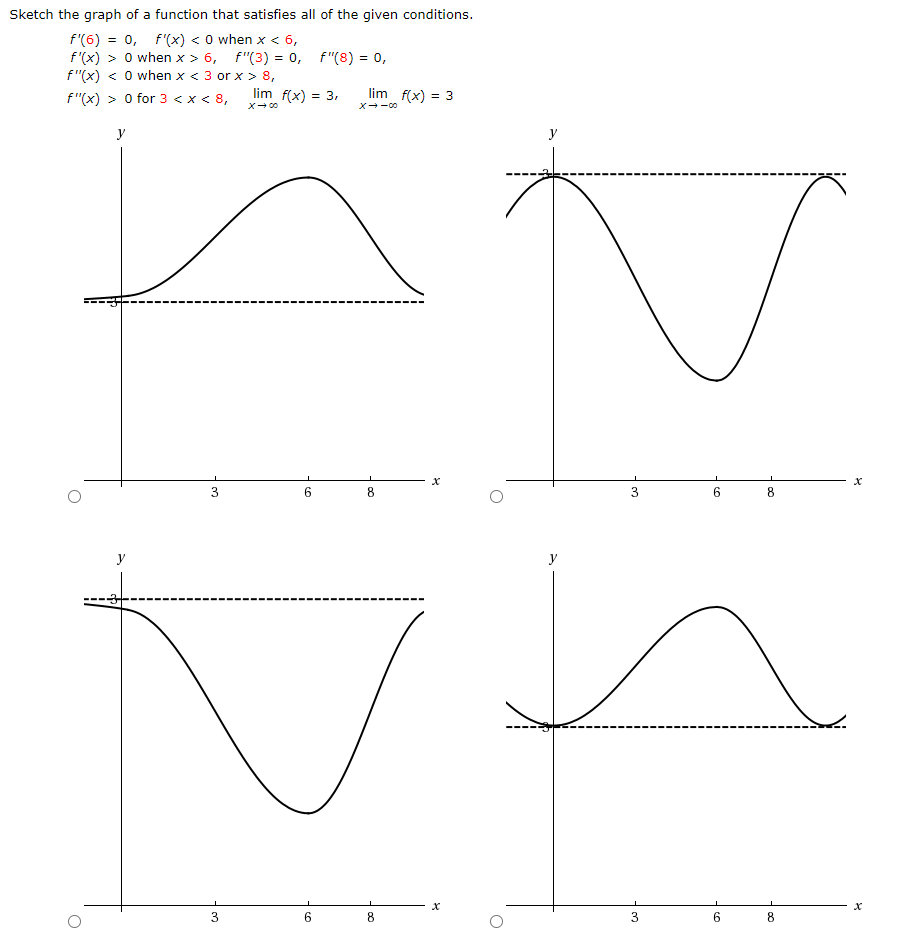



Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com
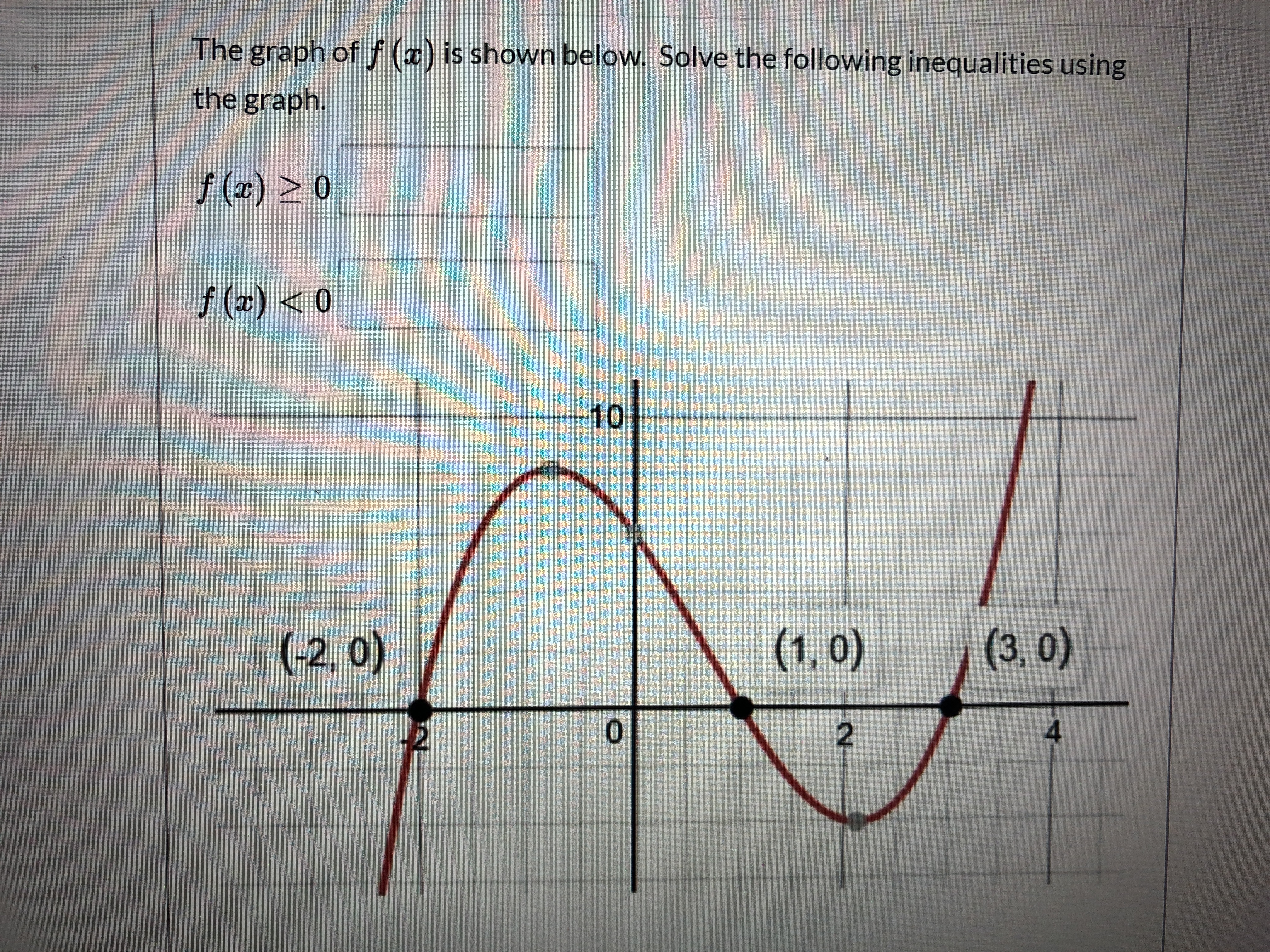



Answered The Graph Of F X Is Shown Below Bartleby




Why Isn T F X X Cos Frac Pi X Differentiable At X 0 And How Do We Foresee It Mathematics Stack Exchange
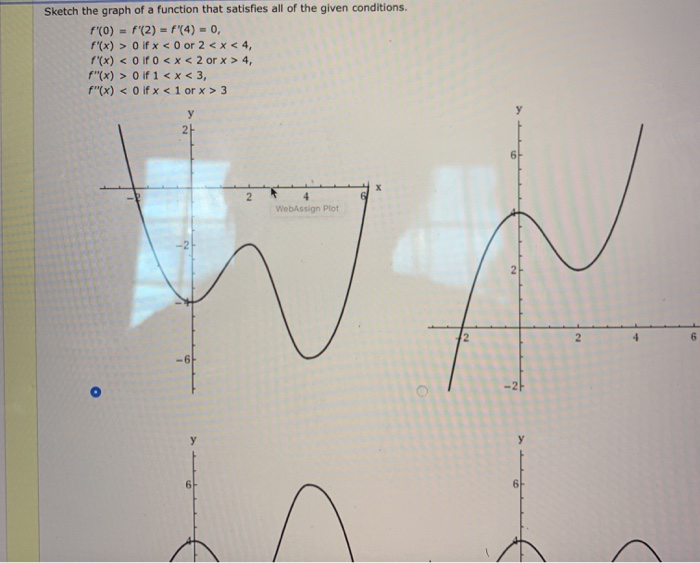



Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com




Illustrations Of Singularities At Point X 0 With The Graph Of The Download Scientific Diagram




The Graph Of Y F X Showing Iteration Points X0 X1 Xi And X2 Download Scientific Diagram



Solving Polynomial Inequalities By Graphing
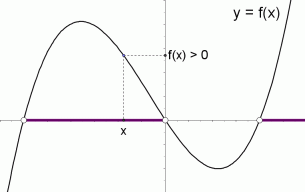



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0



Graph Of A Function Wikipedia



The Function F Is Defined By F X 1 X X 0 1 X 0 X 1 X 0 Draw The Graph Of F X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
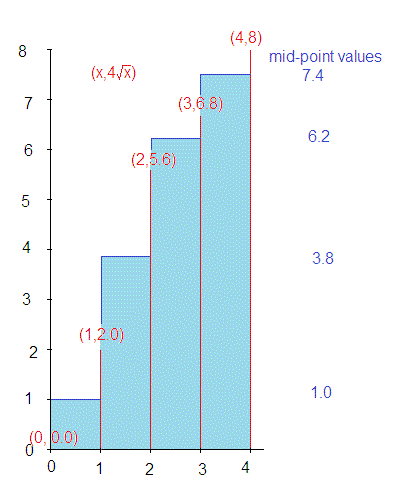



How Do You Estimate The Area Under The Graph Of F X 4sqrt X From X 0 To X 4 Using Four Approximating Rectangles And Right Endpoints Socratic



Curve Sketching F X
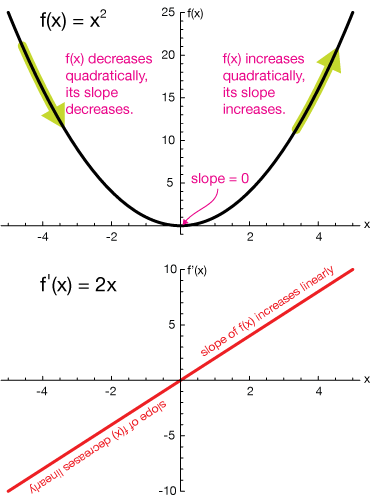



The Derivative




The Graph Of F X Is Given Below Complete The Table Below X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 F X 5 Study Com




Need Answer Asap The Function F X Is Shown On The Graph If F X 0 What Is X Brainly Com
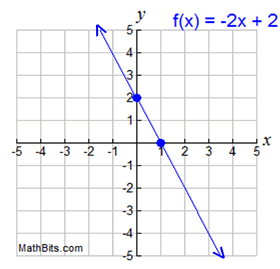



Features Of Function Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
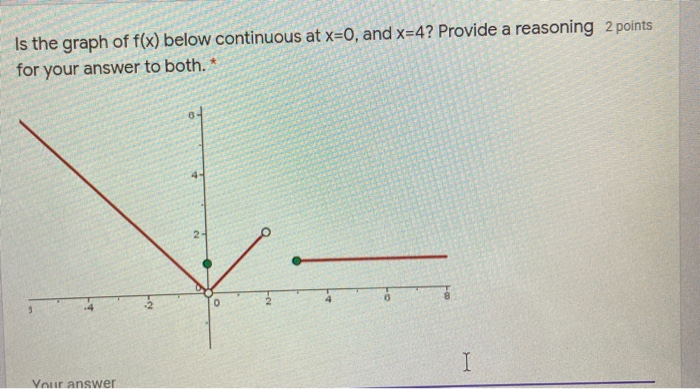



Is The Graph Of F X Below Continuous At X 0 And Chegg Com



Does The Graph Of F X 1 For X 0 0 For X 0 And 1 For X 1 Has A Vertical Tangent At Origin Quora
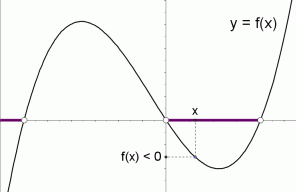



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0




How To Use Graph To Determine Where F X 0 And F X 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




The Graph Of F X Ax 2 All Quadratic Functions Have Graphs Similar To Y X 2 Such Curves Are Called Parabolas They Are U Shaped And Symmetric With Ppt Download




The Graph Of Ln F X For Example 4 1 With X 0 10 Download Scientific Diagram
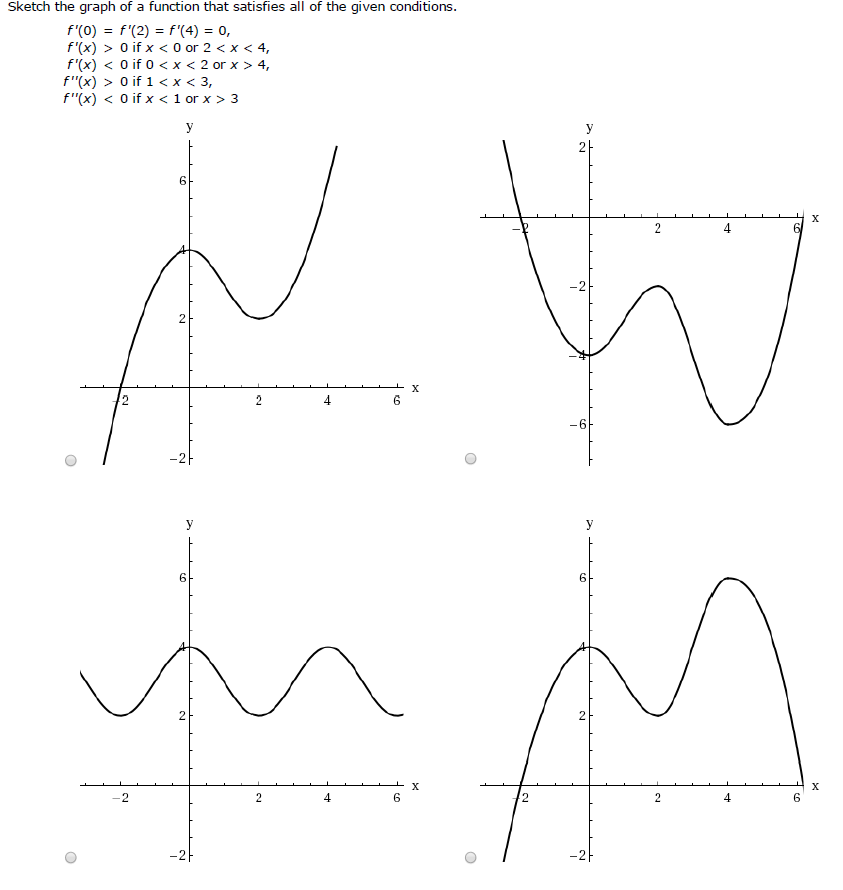



Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com
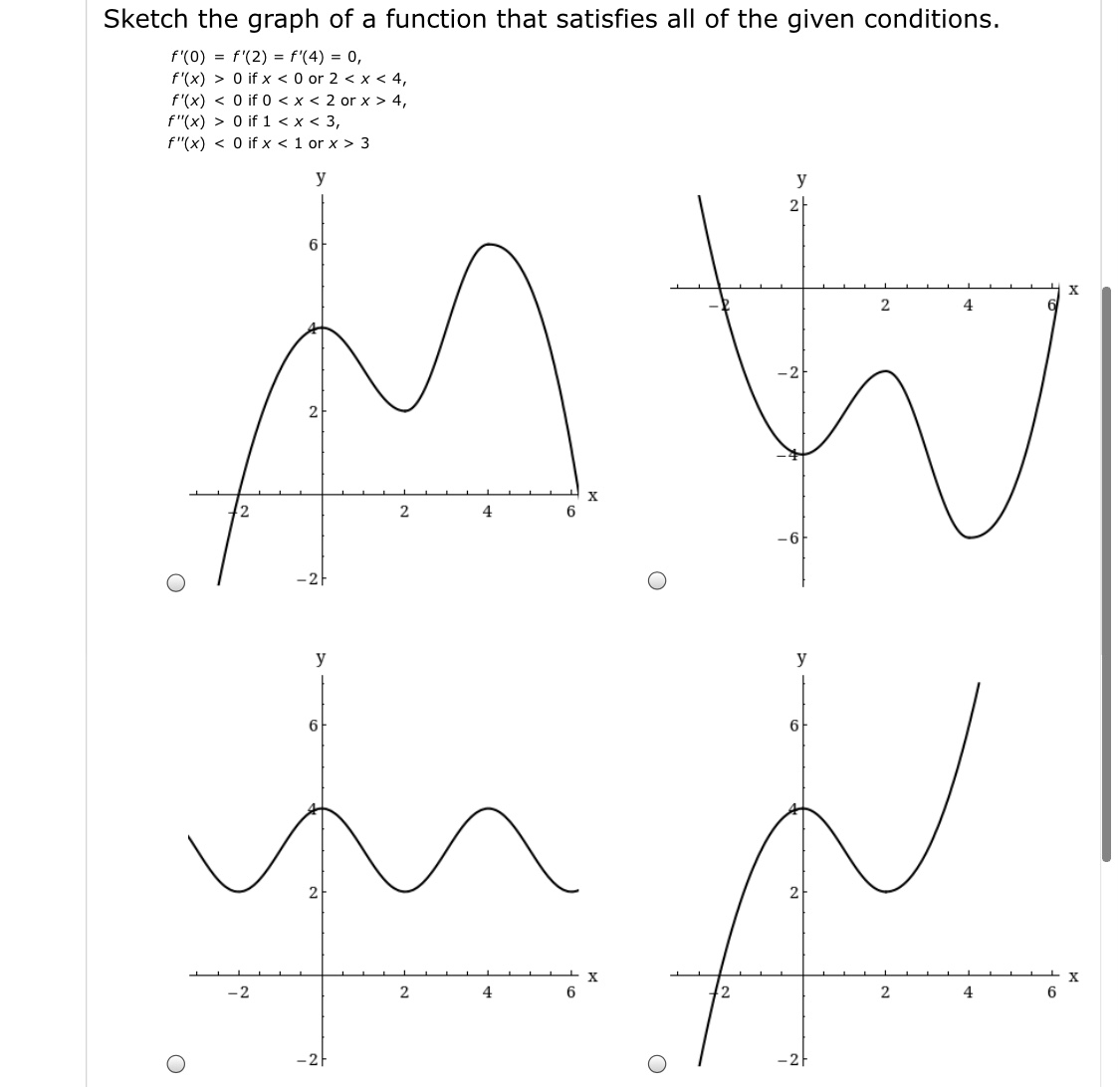



Answered Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Bartleby




Efofex Software




Find The Maximum Value Of F X X 2 1 2x For X 0 Only By Graphing Study Com
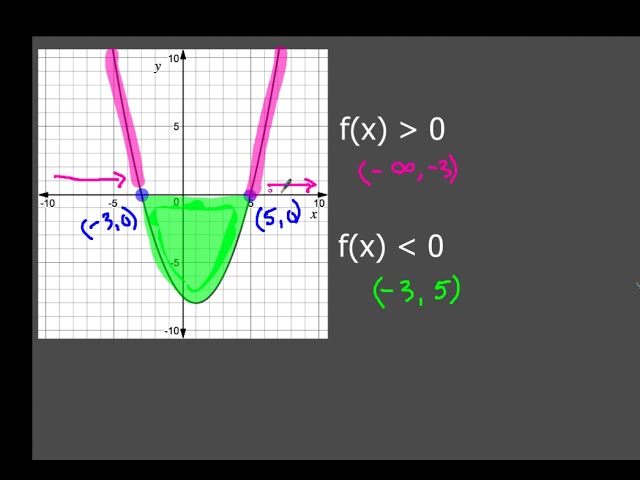



Find The Values Of X For Which F X 0 Youtube
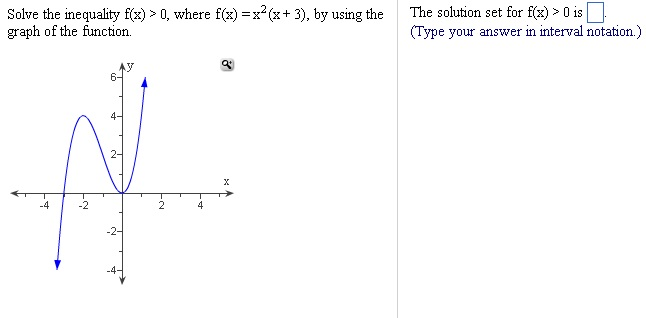



Solve The Inequality F X 0 Where F X X 2 X Chegg Com




Given The Graph Of Y F X Below At Which Of The Marked X Values Can The Following Statements Be True Study Com



What Does F 0 Represent On The Graph Of F X Quora




4 3 How Derivatives Affect The Shape Of A Graph Mathematics Libretexts



Math Ou Edu Forester 1914f14 Hw8 Pdf
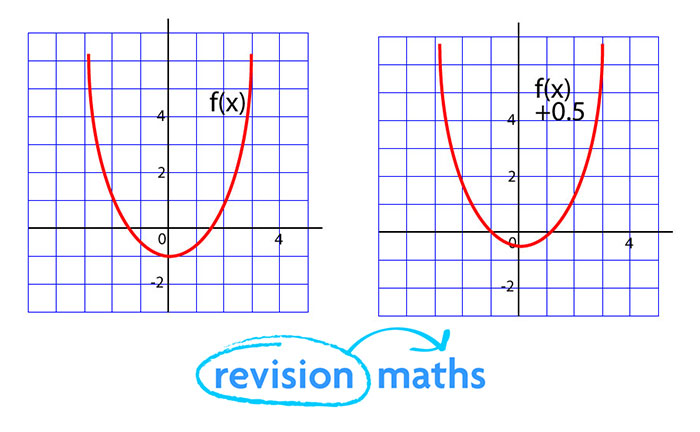



Functions Maths Gcse Revision



No comments:
Post a Comment