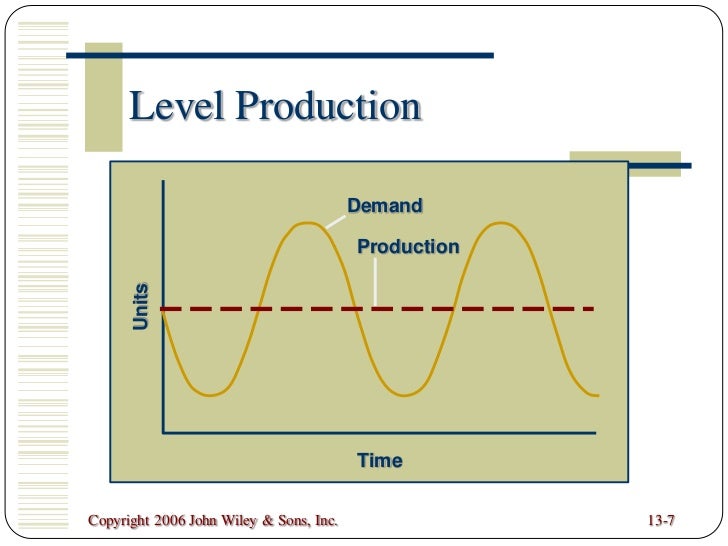
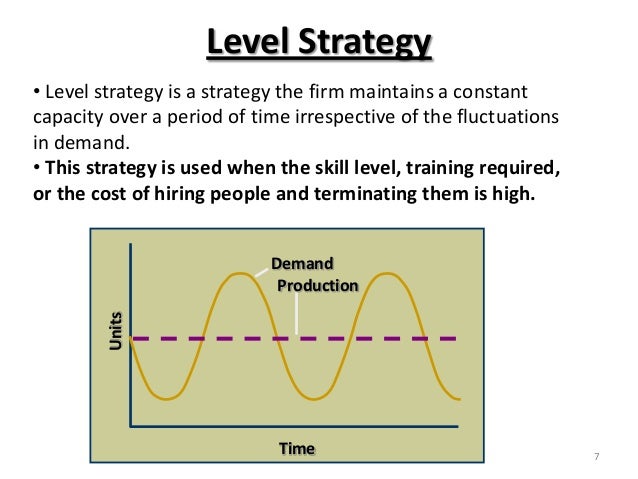
Level Production Strategy We are going to find the requirements for the entire period of the plan and also produce the average amount that is needed per month in order to meet the plan First we are going to determine the total average requirements per month Avg requirements = total number of requirements – opening inv closing inv The capacity of teams, business capabilities and processes This can include human resources, equipment, infrastructure, facilities and technology For example, an operations team plans the resources required to boost production by 10,000 units a day An IT strategy plan is a guiding document for a company's IT organization It defines the overall goals, the strategies that support those goals, and the tactics that are needed to execute those strategies Each section of the IT strategy plan focuses on one strategy and describes specific activities needed to implement that strategy

How To Create A Human Resource Strategy Aihr Digital
Level capacity strategy example
Level capacity strategy example-Marketing Implement new advertising plan Capacity planning is a strategic process whereby a company determines what level of capacity it will need to satisfy the level of demand for



Capacity Planning What Is It And How Do I Implement It Projectmanager Com
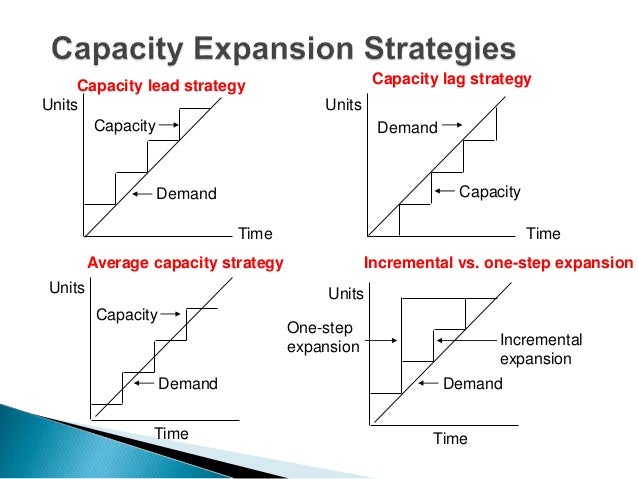
Chase demand strategy can be defined as a strategy where the changes are made to the output according to the demand Here, the changes are in terms of increasing or decreasing the output in line with the rising or falling demand It involves matching the demand by hiring or firing the workers or by controlling the level of production and using The lead strategy tries to anticipate future required capacity and expands capacity to meet it The lag strategy only expands capacity when present capacity is fully used Both have a high risk of not providing required capacity The match strategy closely tracks capacity use and incrementally increases capacity as neededThis problem has been solved!
When dealing with more than one product, it is best to measure capacity in terms of each product For example, the capacity of a firm is to either produce 100 microwaves or 75 refrigerators This is less confusing than just saying the capacity is 100 or 75 Another method of measuring capacity is by referring to the availability of inputsCAPACITY BUILDING STRATEGY The purpose is to achieve a high level of ownership and motivation on the part of GRZ 2 Capacity Assessment/Identification of Gaps/Needs At the beginning of the program, the team conducted capacity assessments to ascertain (For example, the initial capacity building plan targeted nationallevel GRZ staffThe chase strategy has the highest peak capacity requirement This means that facilities, both production and warehousing, will need to be larger than the other two strategies would require In addition, those facilities will not be 100% fully utilized, except for those rare occasions when you are at peak capacity
Capacity is usually measured in convenient units such as litres per hour or passengers per taxi For instance, a domestic tap may be able to deliver litres per minute of water;The steps are in order Evaporation, Wash, Centrifugation, Grinding, Drying, Sack, Packaging, ShippingThe level capacity strategy, the focus is on the process where product output remains at a somewhat fixed level and increases/decreases in demand are satisfied through strategic decisions of utilizing inventory (maintain buffer stock), outsourcing and backorders In comparison to level capacity strategy is adjusting capacity to follow



What Is Strategic Analysis Questionpro



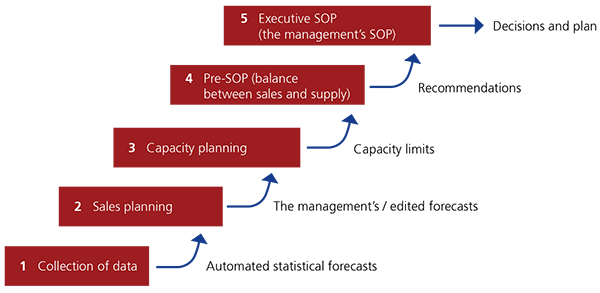
Implementing A Sales Operations Planning S Op Process Plex Demandcaster
Capacity planning is defined as a method to gauge the production capacity needed to meet the changing product demands of an organization Two terms of design capacity and effective capacity are used extensively in the context of capacity planning The first is the maximum work that is completed in a specific period by an organization, and the latter is theLevels of Strategies Once a firm has set its objectives, it then must turn to the question of how it will achieve them A businesslevel strategy is the framework a firm uses to organize its activities, and it is developed by the firm's top managers Examples of businesslevel strategies include cost leadership and differentiation Capacity Planning It's pprove/cancel projects



Aggregate Planning Report




Aggregate Capacity Planning Pdf Free Download
See the answer Subway shops are an example of A level capacity plan A pull strategy Vertical integration A fixedposition layout Low visibilityFunctional level strategies will be specific and will apply to a variety of functional areas (departments) For example, building on the diversification example, the functional level strategies that support that business level strategy might be R&D Redesign product;An example of level capacity management could be the first step of the production of salt by evaporation (in Italy there is one industry like this in Salina) In hot countries, salt is produced by allowing the sun to evaporate sea water in shallow pools or 'pans';




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq



Master Production Schedule
Explain about the level capacity strategy Level capacity strategy The organisation produces or manufactures at a constant rate of output avoiding any changes or fluctuations within customer demand levels This frequently implies stockpiling or higher holdings of inventory while customer demand levels reduceThis revision video provides an overview of the concept of capacity, capacity utilisation and some of the issues facing businesses operating at low or high uCapacity Decisions are Strategic 1 Capacity decisions have a real impact on the ability of the organizationto meet future demands for products and services 2 Capacity decisions affect operating costs 3 Capacity is usually a major determinant of initial cost Typically, the greater the capacity of a productive unit, the greater its cost 4




Maintenance Capacity Planning Ppt Video Online Download




How To Implement Business Capacity Planning Strategies Steps
The Extremes Level Strategy Chase Strategy Production equals demand Production rate is constant Basic Aggregate Planning Strategies for Meeting Demand Level capacity strategy Keeping work force constant and maintaining a steady rate of regulartime output while meeting variations in demand by a combination of options (such as using inventoriesA bus may have a capacity of 53 passengers, a football stadium may be able to seat 50,000 spectators or a McDonalds may be able to serve 600 customers per hourIn other words, Manager A is tied to the "chase demand" strategy, and his counterpart, Manager B in the adjacent office, is locked into the "level capacity" strategy



1




Ms Sample Test Paper 13 Strategic Management Logistics
– Time flexibility from workforce or capacity strategy assumes labor pool can work variable hours (incl overtime), has lower inventory& utilization, – Level strategy – keep capacity & labor usage constant, either stockpile inventory or short orders as needed – Mixed strategy – a combination of one or more of the first three strategiesThe advantages of the level capacity strategy include 1 The utilization of operational resources throughout the year 2 Efficient level of production can be maintained 3 Decreases the marginal cost The disadvantages of the level capacity strategy include 1 If there is any change in the demand of the customer there is a risk of23 Strategic Objective 3 – Technical Capacity 9 24 Strategic Objective 4 – Coordination and Programme Management 12 25 Strategic Objective 5 – Institutionalisation of CD 14 30 Strategy Implementation 15 40 Financing the CD Strategy 18 50 Monitoring the CD Strategy 19




Capacity Management




Doc Capacity Planning Richa Verma Academia Edu
Capacity strategy Is the pattern of decisions concerned with how operations configure and change their capacity in order to achieve a particular level of output potential (See figure 115 and example on page 308) Step 2 Alternative capacity plans (Level capacity plan) 2) Adjust capacity to reflect the fluctuations in demand ( ChaseProvides a high level strategic framework for capacity building within PEPFAR for use by technical working groups and country teams Encourages strategic use of USG resources to develop capacity in the context of overall national strategic plans for HIV and the broader, health sector both public and private Lag strategy is a conservative method of capacity planning that ensures your costs are as low as possible The potential downside to this strategy is that it can create a lag in the delivery of products or services to customers, which is where the name comes from




What Is Capacity Planning Examples Types Optimoroute




Everything About Capacity Planning Strategies Its Benefits
Lag Strategy Waiting until your current capacity is stretched to its limits before adding more capacity For example, a call center with 10 staff that doesn't hire more employees until everyone is working overtime This may serve to boost efficiency and productivity as current resources are heavily utilizedStrategies to Meet Uneven Demand Example Level capacity strategy Chase demand strategy 1) Level capacity strategy The organization manufactures or produces at a constant rate of output ignoring any changes or (rise/fall) in customer demand levels Advantages Utilization of operational resources at all times Efficient production levels can be held at a constant rateLevel Capacity Plan The inventory size is varied keeping the workforce size and utilization of work constant The number of workers ( working size) is kept constant throughout the time period under consideration During months of low demand the excess units required over the units produced are taken from the inventory




Question 4 A Compare And Contrast The Level And Chegg Com




What Is Capacity Planning Examples Types Optimoroute
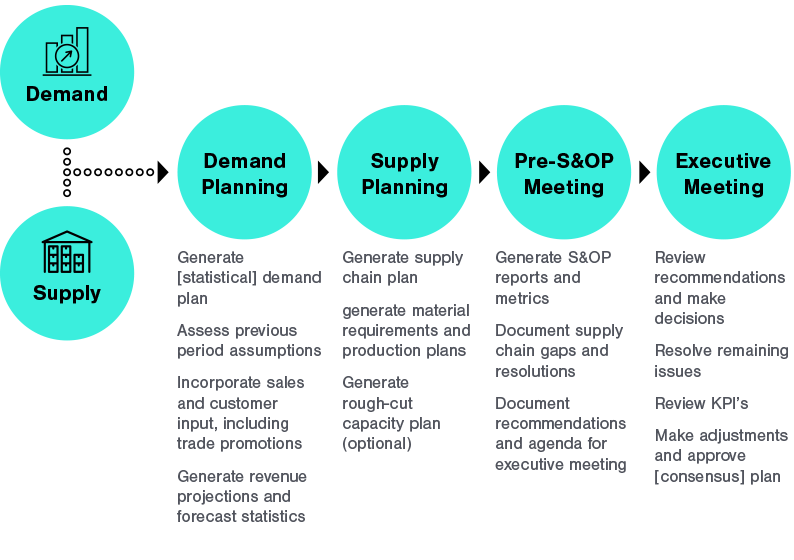
Strategic capacity planning Sales and operations Planning (S&OP) Sales plan Aggregate operations –Examples •labor hours of production •total number of units (in aggregate) –# of cars to make •Level strategy (constant work force, use inventory as buffer) •Chase strategyThe idea here is that a level schedule is used during consistent periods and the chase strategy is used during months with fluctuating demand This can be helpful in seasonal business For example, a company that made Halloween chocolates, may maintain a level schedule for 9 months of the year and then use a chase strategy during the weeks One of the strategic choices that a firm must make as part of its manufacturing strategy There are three commonly recognized capacity strategies lead, lag, and tracking A lead capacity strategy adds capacity in anticipation of increasing demand A lag strategy does not add capacity until the firm is operating at or beyond full capacity



Business Continuity Plan Ready Gov




Basic Strategies Level Capacity Strategy Chase Demand Strategy Ppt Download
Under the chase strategy, production is varied as demand varies With the level strategy, production remains at a constant level in spite of demand variations In companies that produce to stock, this means that finished goods inventory levels will grow during low demand periods and decrease during high demand periodsCapacity is often measured in hours available to be worked by employees And in this context, "planning" is the act of scheduling employee hours against a fixed or expected amount of work Example A company has 10 employees Each employee works 40Capacity Option Changing inventory levels For example, the operations manager can vary workforce levels by hiring or laying off, or can vary production by means of overtime, idle time, part time employees, or subcontracting In other words, a level strategy is an aggregate plan in which production is uniform from period to period




Sap Pp Capacity Planning Cm01 Cm21




4 Steps To Strategic Human Resource Planning Lucidchart
Capacity planning strategy involves the process used to determine the resources manufacturers need to meet the demand for their products or services The level of capacity directly relates to the amount of output in the form of goods and services manufacturers can produce to satisfy customer demand Capacity planning strategies can guide An approach to aggregate planning that attempts to match supply and output with fluctuating demand Depending on the product or service involved, the approach can incur costs by the ineffective use of capacity at periods of low demand, by the need to recruit or lay off staff, by learningcurve effects, and by a possible loss of quality The advantages include low storageAt the individual level, capacitybuilding involves establishing the conditions under which public servants are able to embark on a continuous process of learning and adapting to change — building on existing knowledge and skills and




What Is Corporate Level Strategy Definition Salient Features And Classification Business Jargons




Examples Of Strategic Tactical And Operational Decisions Download Scientific Diagram
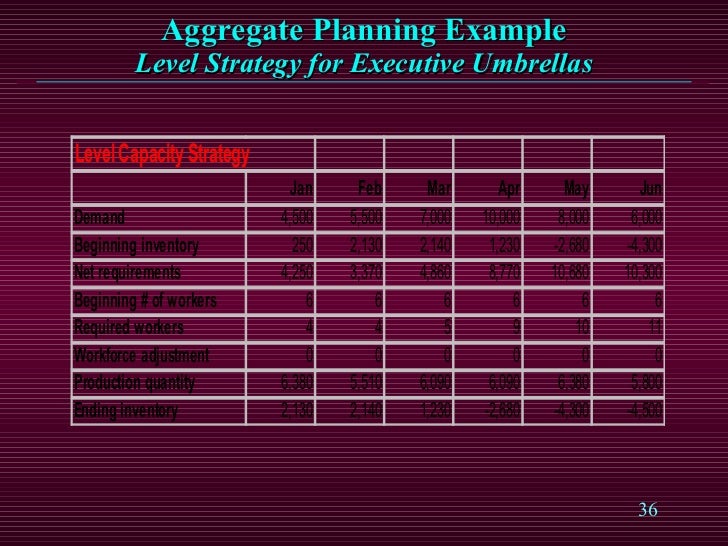
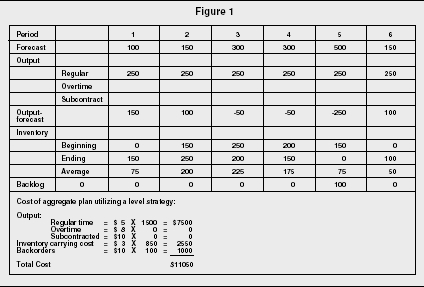
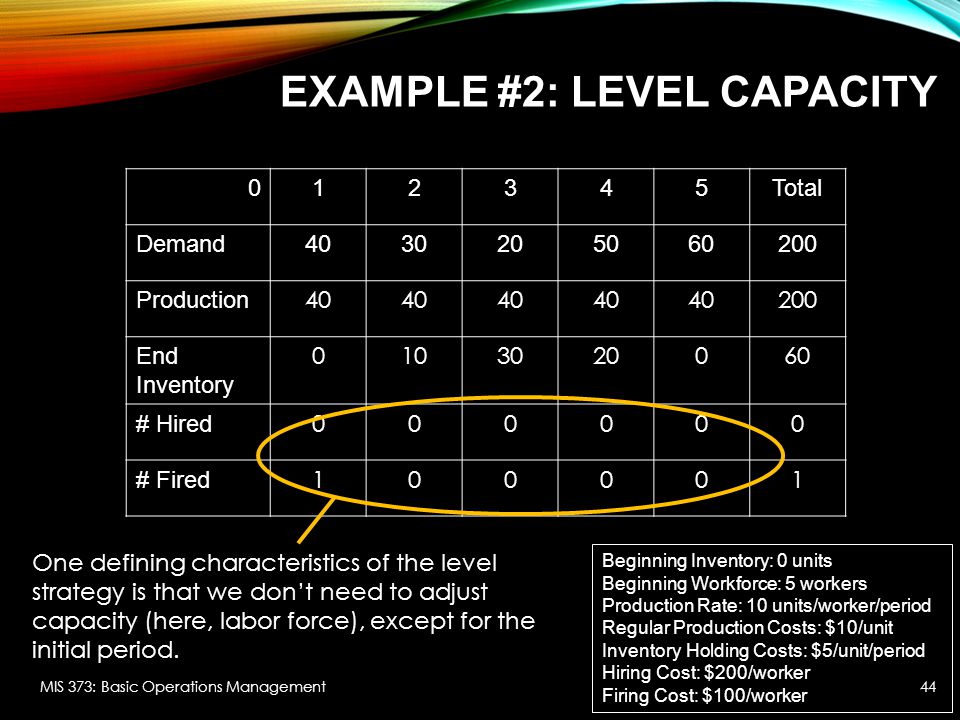
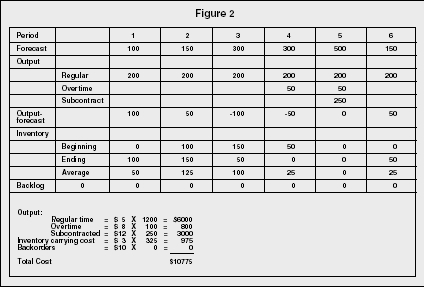
LEVEL STRATEGY A level strategy seeks to produce an aggregate plan that maintains a steady production rate and/or a steady employment level In the context of the problem posted by you following the level strategy means incurring additional subcontracting costs at least twice This is to offset the shortfall in production because of the levelInputs Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 Forecasted demand (Number of parttime workers 6 12 18 15 13 14 Example 1 Level strategy Each period is hours • From the beginning



Sales Amp Operations Planning




Capacity Planning What Is It And How Do I Implement It Projectmanager Com




Capacity Planning Meaning Classification And Its Goals




Competitive Advantage Tutor2u



Hr Un Org Sites Hr Un Org Files 4 5 1 6 Strategic planning guide 0 Pdf



Aggregate Planning Strategy Organization Levels System Examples Model Type Company System




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq



Http Aeconf Com Articles May17 Aef Pdf




Evaluating Capacity Development Better Evaluation



Quick Guide How To Write A Strategic Plan Smartsheet



Researchportal Port Ac Uk Portal Files Boydell 11 Pub Ch7 Capacity Planning And Management Pdf
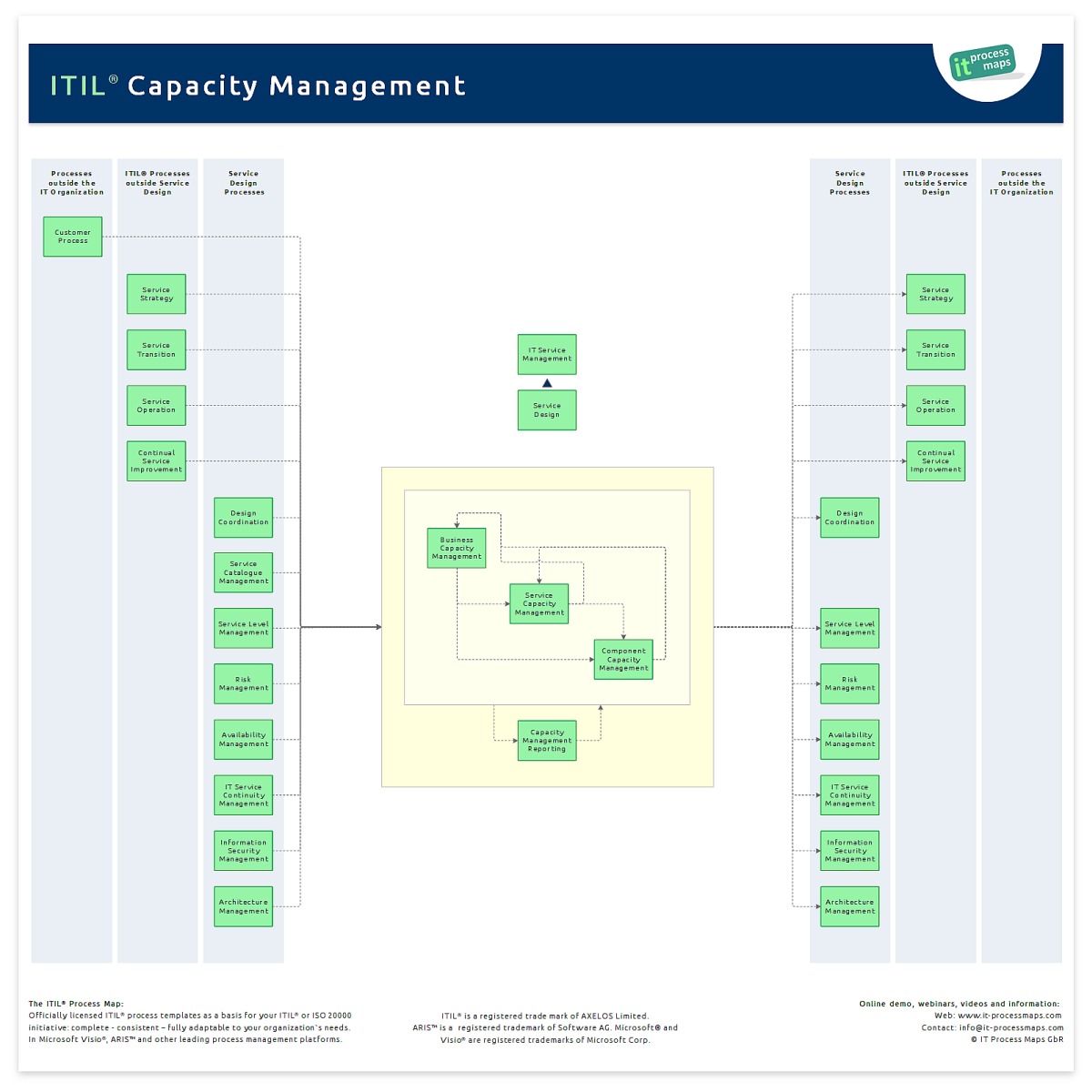



Capacity Management It Process Wiki




Coronavirus S Impact On Supply Chain Mckinsey




Itil Capacity Management Bmc Software Blogs




Examples Of Strategic Tactical And Operational Decisions Download Scientific Diagram




What Is Organizational Development A Complete Guide Aihr Digital
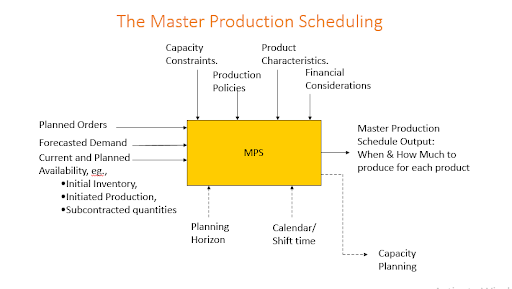



Inventory Management 101 The Master Production Schedule Mps Explained Optipro Software




How To Create A Sales Plan Template Examples




Operations Management Ppt Video Online Download




How To Create A Human Resource Strategy Aihr Digital




How To Implement Business Capacity Planning Strategies Steps



A Complete Strategy Map Template Including Examples Clearpoint Strategy




Quick Guide How To Write A Strategic Plan Smartsheet




Action Plan Federal Data Strategy
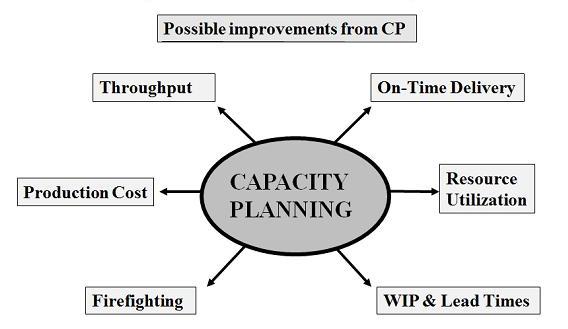



Concept Of Capacity Planning And It S Procedure Importance Management Study Hq
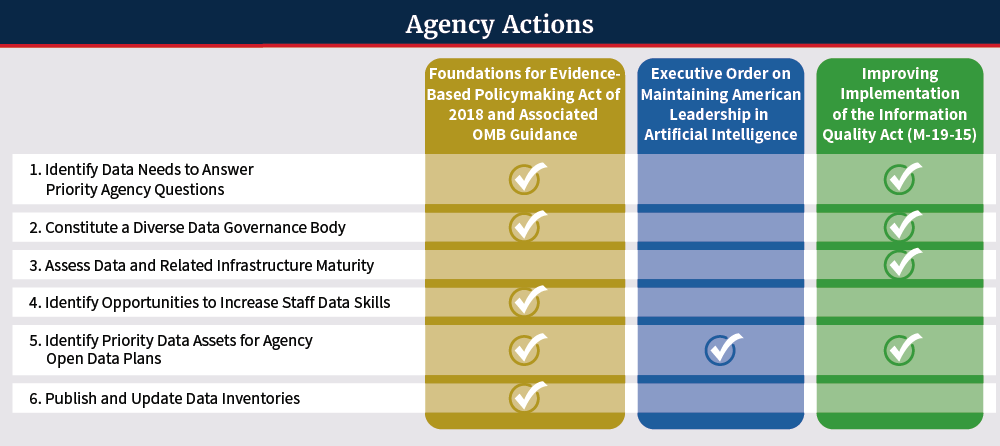



Action Plan Federal Data Strategy
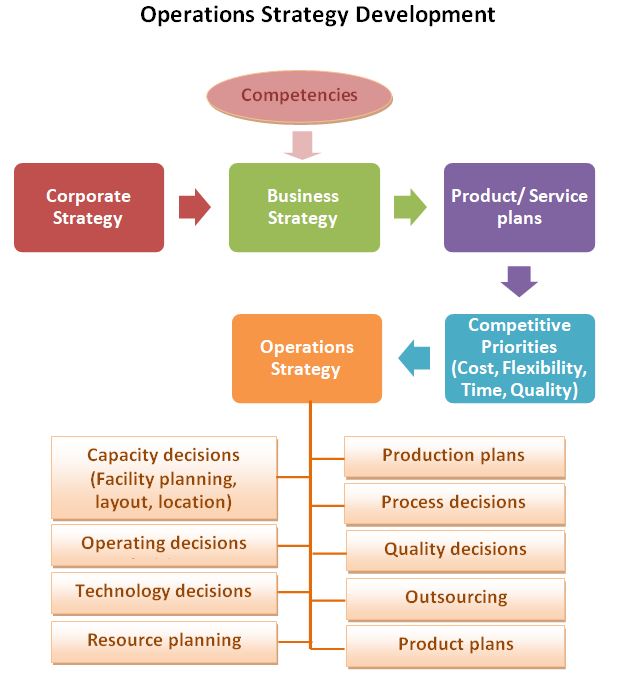



Operations Strategy With Examples Studiousguy




What Is Capacity Planning Examples Types Optimoroute




Strategy Under Uncertainty




Strategic Capacity Planning Introduction To Operations Management



1




Strategic Capacity Planning Introduction To Operations Management




4 Steps To Strategic Human Resource Planning Lucidchart




Entries For Thursday 25 October 07 Sergio S Blog




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq




Capacity Planning Types Lead Lag Average Strategies Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Capacity Planning Everything You Need To Know Clicktime




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq



What Is Capacity Planning Examples Types Optimoroute




Capacity Utilization Manufacturing Kpi Examples Sisense
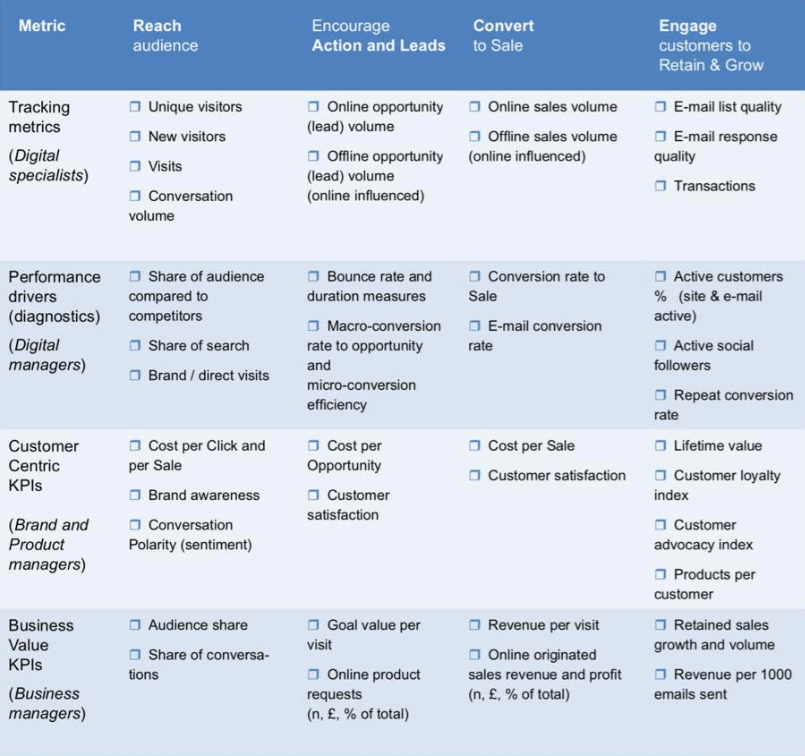



Strategic Analysis Your Ultimate Guide Marketing Templates



Models Of Aggregate Planning



Capacity Management



Sales And Operations Planning Relex Solutions



1



Capacity Planning What Is It And How Do I Implement It Projectmanager Com




Operations Strategy Capacity Strategy Ppt Video Online Download



Is Muni Cz El Econ Jaro09 Phom Um Chapter 11short Pdf
.PNG)



Process Landscape Aris Bpm Community



Master Production Schedule




Operations Strategy With Examples Studiousguy




Capacity Planning Meaning Strategies Importance And Procedure



Capacity Utilization Definition Example And Economic Significance



Aggregate Planning Strategy Organization Levels System Examples Model Type Company System




Strategic Themes Scaled Agile Framework




Evaluating Capacity Development Better Evaluation




Covid 19 Models For Hospital Surge Capacity Planning A Systematic Review Disaster Medicine And Public Health Preparedness Cambridge Core



3




Capacity Planning Meaning Strategies Importance And Procedure



Aggregate Planning Chapter 11 Mis 373 Basic Operations Management Ppt Download




Capacity Planning Everything You Need To Know Clicktime



Balancedscorecard Org Wp Content Uploads 19 08 Bsi Strategic Themes E2 80 93how Are They Used And Why Pdf




Strategic Capacity Planning Introduction To Operations Management




Common Types Of Corporate Strategies Boundless Management




Capacity Building Wikipedia




When Using A Level Capacity Strategy Or Level Chegg Com




How To Implement Business Capacity Planning Strategies Steps



9 Business Roadmap Examples For Scaling Your Organization




Capacity Planning Organization System Examples Definition System Long Term Capacity Planning




Sap Pp Capacity Planning Cm01 Cm21



Strategic Goal Examples For Use In Your Strategic Plan And Balanced Scorecard




Porter S Generic Competitive Strategies



Aggregate Planning Strategy Organization Levels System Examples Model Type Company System




R K Strategies Bioninja



Is Muni Cz El Econ Jaro09 Phom Um Chapter 11short Pdf




Strategic Capacity Planning Capacity Utilization
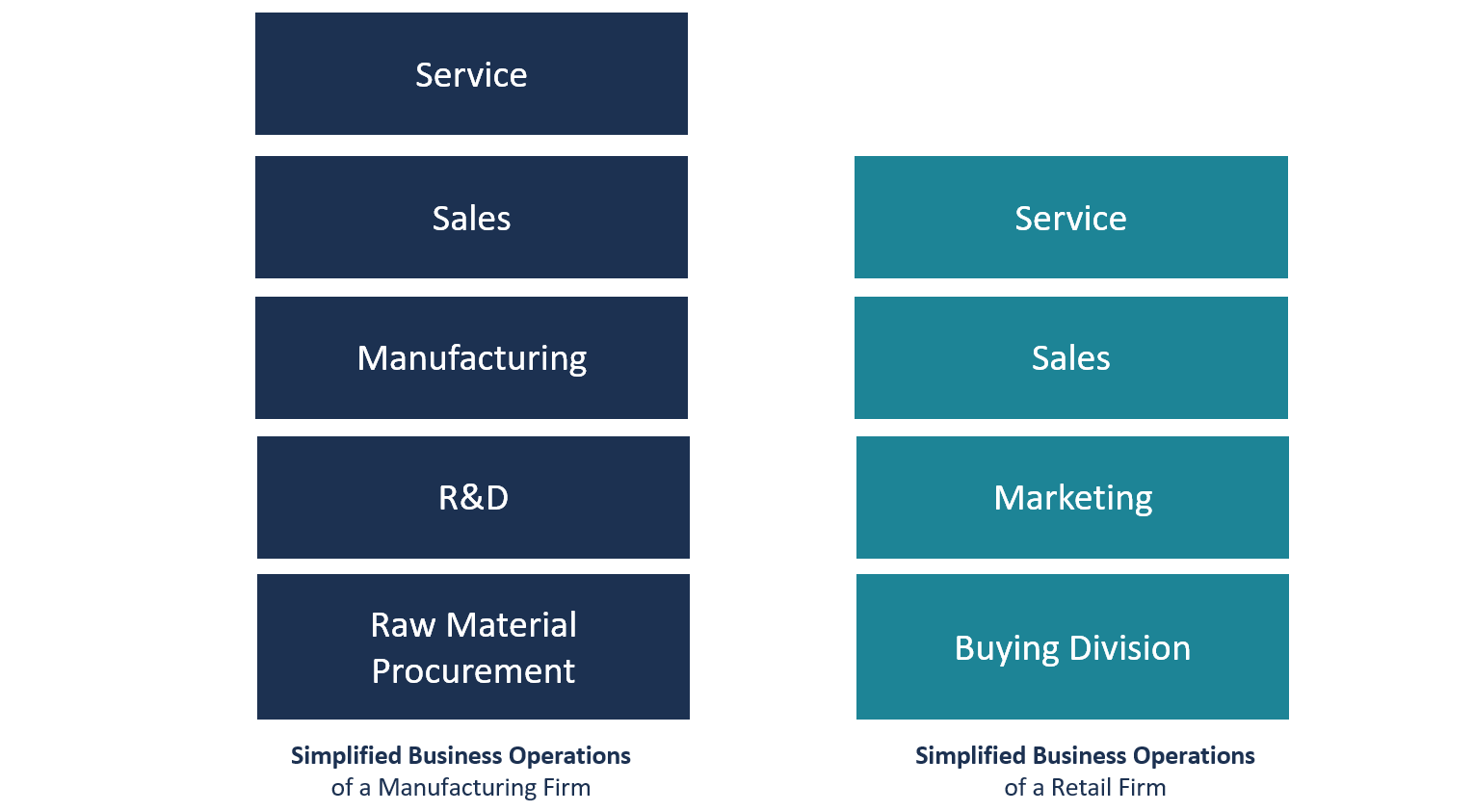



Business Operations Overview Examples How To Improve



How To Build Career Pathways At Your Organization The Management Center




Everything About Capacity Planning Strategies Its Benefits
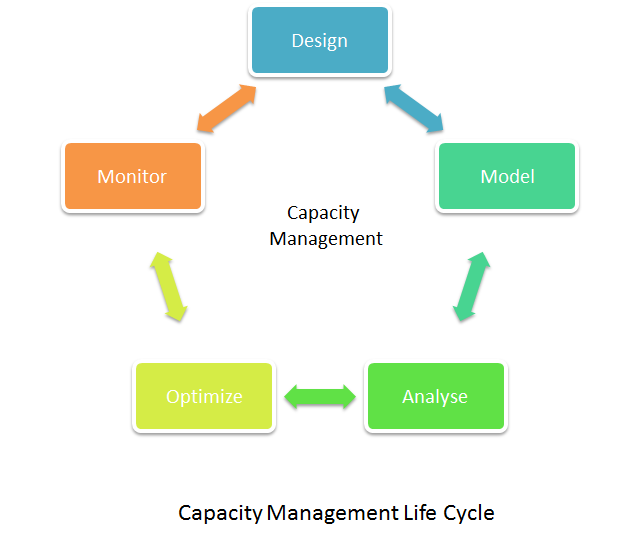



What Is Capacity Management Definition And Faqs Omnisci



Capacity Planning Everything You Need To Know Clicktime



Strategic Capacity Planning Aggregate Planning Ppt Video Online Download



No comments:
Post a Comment